Back to: Botany 500 Level
My Afrilearn superstar, how far today?
I trust say you dey do well and full of energy! Today, we go do something different but exciting. We go talk about Mini Fieldwork: Vegetation Mapping. This topic na one wey go help you get practical knowledge about how scientists and ecologists go out into nature to study plants and their environment. You dey ready? Let’s explore this cool way to learn more about plants and their habitats.
Mini fieldwork: vegetation mapping
What Is Vegetation Mapping?
Vegetation mapping na the process wey people use to map or draw out the types of plants (vegetation) wey dey grow in a particular area. It’s like drawing a big picture of the plants and where they dey located in an environment, helping us to understand which plants grow where and how they interact with their surroundings.
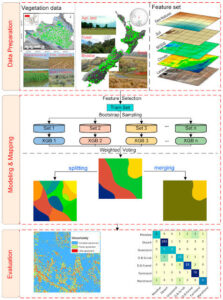
In vegetation mapping, scientists use tools and techniques to observe the plants in an area, record their types, and plot them on a map. This helps to study the distribution of plants, the health of the ecosystem, and how the environment affects plant growth.
Why Is Vegetation Mapping Important? Vegetation mapping dey very important for many reasons, including:
- It helps us understand plant diversity in different ecosystems.
- It helps to track changes in the environment, like climate change, which might affect where plants grow.
- It supports conservation efforts by identifying areas that need protection.
- It helps to monitor human impacts on the environment, like deforestation or urban development.
Through vegetation mapping, we get to see how different plant species live together and how they depend on each other and the environment to survive. This is why it’s a major tool in studying ecology.
How to Do Vegetation Mapping (Mini Fieldwork)
If you want to try this out for yourself, here’s a simple step-by-step guide for your mini fieldwork. Get ready to explore nature and understand it better!
- Choose a Study Area:
Find a small area, like a part of your garden, school, or even a local park. The area should be large enough to contain different types of plants but small enough for you to observe in detail. - Identify the Vegetation:
Go into the field and identify the different plants growing there. Take note of their species (names), their size, and their location. You can use a plant identification book or app to help you. Don’t forget to look at trees, grasses, shrubs, and even small flowers. Record the types of plants you find. - Map the Area:
Using paper and pencil, draw a map of your area. Start by outlining the boundaries of the space you’re studying. Then, plot the location of each plant species on the map. You can use symbols or colour codes for each type of plant to make it clear. - Record Details:
For each plant species, write down some key details like:- The number of plants in that area.
- Their height, size, and spread.
- Whether they are growing close to each other or far apart.
- Any environmental factors like whether they are in the shade, near water, or exposed to the sun.
- Analyse the Results:
Once you’ve finished mapping, look at the patterns. Are certain plants found together? Do they prefer specific locations in the area? You can draw conclusions about how the plants are interacting with their environment and with each other. For example, some plants may thrive in the shade, while others prefer the sunlight.
Example of a Vegetation Mapping Study
Imagine you go to a local park and map out the vegetation there. You find that the area near the riverbank has tall grasses, shrubs, and water-loving plants. Further from the river, you find taller trees like mango and pawpaw, and in the dry areas, you notice smaller shrubs like bitter leaf and wild basil. From this, you can see that the plants are adapting to the different water and sunlight conditions in the park.
Why Is This Important for You?
Doing vegetation mapping helps you connect to nature in a deeper way. You’ll understand how different plant species relate to each other and their environment, and you’ll get a first-hand view of how ecology works. By mapping vegetation, you also contribute to science, especially in your local area. Your fieldwork might even help in future research or conservation efforts, especially if we notice a decline in plant species or habitat loss.
Summary:
- Vegetation mapping involves identifying and recording the types of plants in a specific area and plotting them on a map.
- It helps scientists and ecologists understand the distribution of plants, how they interact with their environment, and how the environment affects their growth.
- By doing mini fieldwork, you can learn more about local plant species, their habitats, and how they fit into the ecosystem.
Evaluation:
- What are the key steps in doing vegetation mapping?
- Why is it important to study vegetation in an area?
- In your opinion, how can vegetation mapping contribute to conservation efforts?
Well done, my Afrilearn superstar!
You’ve just unlocked a new skill—mapping vegetation! You now know how to observe plants, record their details, and understand how they live and grow in their environments. This hands-on experience makes you a real-life ecologist in the making! Keep up the fantastic work, and I can’t wait for you to share more of your fieldwork stories. Let’s keep pushing forward together!
