Back to: Botany 500 Level
My Afrilearn champion, how you dey today?
I dey salute you specially because you dey learn serious science wey concern the survival of plants—even when life no dey soft for them. Today’s topic na Plant Adaptations to Environmental Stress. Na this kind knowledge go make you respect how smart and powerful plants truly be. Imagine say you dey live for hot desert, dry harmattan, or salty water and you still dey shine—plants dey do am every day!
Plant adaptations to environmental stress
Wetin Be Environmental Stress?
Environmental stress na any condition wey make life hard for plants. E fit be too much heat, small water, salty soil, lack of nutrients, or even human wahala like pollution and cutting down forests. But guess what? Plants no dey just give up—they get correct ways wey dem don adapt to survive.
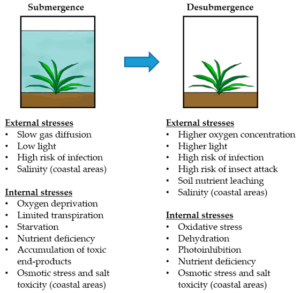
Make we look the common types of stress and how plants handle dem, especially for we African environment.
- Drought (Lack of Water)
Some areas like the northern part of Nigeria fit go for months without rain. Water scarce, sun dey hot like fire. But some plants don wise.
Adaptations:
- Thick leaves or stems to store water (e.g., Aloe vera, cactus)
- Small or no leaves to reduce water loss (e.g., acacia tree)
- Deep roots to reach underground water (e.g., baobab tree)
- Closing stomata during the day to prevent water loss
Na like person wey save money during dry season—na survival strategy!
- High Temperature/Heat
Places like Sokoto dey experience serious heat. Some plants get ways to cope with am.
Adaptations:
- Hairy or waxy leaves to reflect sunlight
- Light-coloured leaves to reduce heat absorption
- Sunken stomata to reduce water loss
- Protective bark to prevent overheating
- Poor or Salty Soil
Some places like near ocean areas or irrigation farms get salt for soil. Ordinary plants no fit survive there, but others don adapt.
Adaptations:
- Salt glands to remove excess salt (e.g., mangroves)
- Storing salt in older leaves wey go drop later
- Thick cuticles to prevent water loss
- Air roots (pneumatophores) to breathe in flooded, salty areas
- Flooding or Too Much Water
In places like the Niger Delta, water dey too plenty sometimes. Roots no dey get enough oxygen.
Adaptations:
- Aerial roots that rise above water (e.g., mangroves)
- Hollow stems or tissues (aerenchyma) to carry oxygen
- Floating leaves to get sunlight and air (e.g., water lily)
- Nutrient Deficiency
Sandy or overused soils fit lack nutrients. Plants still dey try survive.
Adaptations:
- Symbiosis with fungi or bacteria to get nutrients (e.g., legumes and nitrogen-fixing bacteria)
- Carnivorous behaviour – some plants catch insects to get nutrients (e.g., Drosera, Venus flytrap – rare but real!)

Na Like Nigerian Hustle—Plants Dey Adapt to Survive!
Whether na dry soil, too much water or heat, plants dey show resilience pass as you go imagine. Dem dey turn problem into opportunity—real MVPs of nature!
Summary:
- Environmental stress na anything wey make survival hard for plants.
- Common stress types: drought, heat, poor soil, salinity, and flooding.
- Plants adapt through storage tissues, deep roots, hairy leaves, aerial roots, salt glands, and more.
- These adaptations help plants survive and reproduce even under harsh conditions.
Evaluation:
- Mention two ways plants adapt to drought.
- How do mangroves survive in salty environments?
- Give one example of a plant adaptation to flooding.
Kai, you too sabi! My Afrilearn brainbox, you dey on fire!
E sweet me say you dey understand how nature dey arrange survival plans for plants. With this kind knowledge, you go fit tackle any ecology question like pro. Continue dey grow—na you we dey count on for the future of science in Naija! Next lesson dey wait!
