Back to: Botany 400 Level
My brilliant Afrilearn scholar, welcome back! I hope you’re having a fantastic day! Have you ever wondered why a coconut tree stands tall while a pumpkin plant spreads along the ground? Or why some plants have broad leaves while others have needle-like ones? These differences are not by accident—every part of a plant is designed for a specific function. Today, we’ll be looking at the relationship between structure and function in plants and how their form helps them survive and thrive.
Relationship between structure and function in plants
Imagine you’re holding a corn cob and a mango fruit. The corn kernels are protected by husks, while the mango has a fleshy outer layer. Both are fruits, but they have different structures because they serve different functions. The corn needs protection for its seeds, while the mango needs to attract animals to help spread its seeds.
Just like in humans, where the structure of our hands allows us to hold objects and our legs help us walk, plants also have structures that are suited to their functions. The shape, size, and arrangement of plant organs—roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits—are all tailored to help the plant survive in its environment.
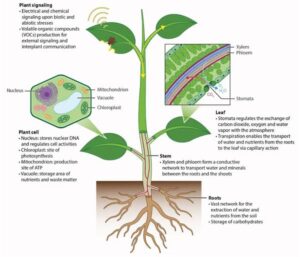
Relationship Between Structure and Function in Plants
Roots: Anchors and Absorbers
The structure of a plant’s roots is designed to help it absorb water and nutrients while anchoring the plant firmly in the soil.
Fibrous roots (like those in grasses) spread widely and help prevent soil erosion.
Taproots (like in carrots and cassava) grow deep to reach underground water sources and store food.
Stems: Support and Transport
Stems provide structural support and transport water, nutrients, and food between roots and leaves.
Herbaceous stems (like in maize) are soft and flexible, allowing quick growth.
Woody stems (like in iroko trees) are strong and rigid, providing long-term support.
Leaves: Factories of Food Production
Leaves are designed for photosynthesis, where they use sunlight to make food.
Broad leaves (like in banana plants) have a large surface area to absorb more sunlight.
Needle-like leaves (like in pine trees) reduce water loss in dry conditions.
Flowers: Attractors for Pollination
Flowers contain reproductive organs that ensure the plant’s survival by attracting pollinators.
Bright-coloured flowers (like hibiscus) attract bees and butterflies.
Wind-pollinated flowers (like maize) are usually small with no scent or bright colours.
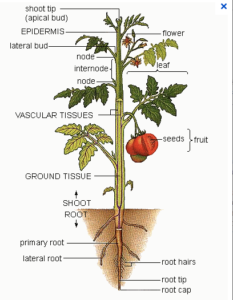
Fruits and Seeds: Protection and Dispersal
Fruits protect seeds and help in their spread.
Fleshy fruits (like mango and pawpaw) attract animals that eat and spread their seeds.
Dry fruits (like groundnuts) protect seeds until they find a suitable place to grow.
Think of a coconut tree and a tomato plant. The coconut has a tall, strong stem and deep roots because it grows in coastal areas where strong winds blow. Meanwhile, the tomato plant has a weak stem that needs support, but its bright red fruit attracts animals for seed dispersal.
Another example is water lilies and desert cacti. Water lilies have broad, flat leaves that float on water, allowing them to absorb sunlight. Cacti, on the other hand, have spiny leaves to reduce water loss and thick stems to store water, helping them survive in dry conditions.
Summary
The structure of a plant determines its function. Roots anchor and absorb nutrients, stems provide support and transport, leaves make food, flowers help in reproduction, and fruits protect seeds. Different plants have structures suited to their environments, ensuring survival and growth. Understanding this relationship helps us appreciate nature and improve agricultural practices.
Evaluation
- How does the structure of roots help in their function?
- Why do desert plants have needle-like leaves instead of broad ones?
- How does a plant’s stem contribute to its survival?
- Give two examples of plants with different leaf structures and explain their functions.
You are doing an amazing job! Learning is a journey, and you are making great progress! Keep asking questions and observing the plants around you—you’ll be surprised at how much they can teach you. I’m so proud of you, and I can’t wait to see you in the next lesson. Keep shining!
