Back to: Botany 500 Level
Hello my Afrilearn superstar! How far today?
I hope say you dey do well, and you’re ready for another exciting topic! Today, we go talk about something that is both modern and very important in the study of ecology—Remote Sensing and GIS in Ecology. Sounds interesting, right? These tools are like the “superpowers” that help scientists study the environment from far away, without needing to be right there. You ready? Let’s go!
Remote sensing and GIS in ecology
What Is Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing na the process of collecting information about an object or an area without being in physical contact with it. Instead of being right there to observe plants, animals, or landforms, remote sensing uses special tools like satellites, drones, or aircraft to collect data from a distance.
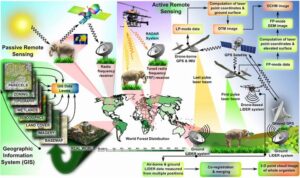
Imagine you are using a drone to take pictures of a forest. From the drone, you can see large areas, and with the right sensors, you can detect things like tree health, water availability, and even how much sunlight an area is getting. This is what remote sensing helps us do in ecology—observe and monitor large, hard-to-reach areas with minimal effort.
Why Is Remote Sensing Important in Ecology?
Remote sensing is really important for studying ecology because it gives scientists a way to:
- Monitor large areas: With remote sensing, we can observe wide regions that are hard to get to, like forests, wetlands, or even remote deserts.
- Track environmental changes: Whether it’s deforestation, pollution, or land use changes, remote sensing can help track how these things are happening over time.
- Study habitat changes: We can monitor how habitats for plants and animals are changing, whether through natural causes like wildfires or human impacts like urban expansion.
Example:
In Nigeria, remote sensing is used to monitor the health of the Niger Delta region. Scientists use satellite imagery to detect changes in the water levels, vegetation, and land use, which can help identify areas at risk of flooding or pollution.
What Is GIS?
GIS (Geographic Information System) is a tool that allows you to store, analyse, and display geographic data. While remote sensing gives you the data (like satellite images), GIS is the system that helps you organise and understand that data.
GIS works by combining maps and data layers. For example, you can combine layers showing soil type, water availability, and vegetation type in one map. This makes it easier to study how different factors like rainfall, temperature, and soil quality are influencing the distribution of plants and animals in a particular area.
Why Is GIS Important in Ecology?
GIS is super useful for ecology because it allows scientists to:
- Analyse patterns: Scientists can use GIS to look at how plant species or animal populations are distributed in different areas, and how they relate to things like climate or human activities.
- Plan conservation strategies: By mapping out areas where biodiversity is most at risk, GIS helps identify the best places to focus conservation efforts.
- Visualise complex data: GIS turns complex ecological data into easy-to-understand maps and visuals, making it easier to see patterns and trends.
Example:
In Nigeria, GIS has been used to map out the distribution of African elephants in the Yankari Game Reserve. This helps park managers track where the elephants are located, which areas need more protection, and how human activities around the reserve might be affecting their movement.
How Do Remote Sensing and GIS Work Together?
Remote sensing and GIS work hand-in-hand to help ecologists get a full picture of the environment. Here’s how:
- Data Collection: Remote sensing collects data from satellites or drones, giving scientists pictures of the land.
- Data Analysis: GIS is used to analyse and interpret the data collected. This helps ecologists understand how the environment is changing and how different factors are interacting.
- Decision Making: By combining data from remote sensing and GIS, scientists can make better decisions about conservation, land use, and other ecological management practices.
Example:
Let’s say you’re studying a forest reserve in Nigeria. Remote sensing satellites can give you regular images of the forest to show changes in vegetation. Then, you use GIS to combine that data with other factors like soil types, rainfall, and elevation. With this, you can easily identify which areas of the forest are most at risk of deforestation, which areas need more protection, and how the forest’s health is changing over time.
Summary:
- Remote sensing helps gather data about an area from a distance, using tools like satellites and drones.
- GIS (Geographic Information System) helps organise, analyse, and visualise geographic data, making it easier to study patterns in ecology.
- Both tools work together to monitor environmental changes, track biodiversity, and support conservation efforts.
Evaluation:
- What is remote sensing, and why is it important in ecology?
- How does GIS help in ecological studies?
- How do remote sensing and GIS work together to support conservation efforts?
Well done, my Afrilearn superstar!
You’ve just learned about two powerful tools that are helping scientists study the environment and protect nature from afar—Remote Sensing and GIS. These tools allow us to monitor large areas, track environmental changes, and make better decisions for conservation. Keep up the amazing work, and stay excited for more learning ahead. You are definitely on the path to becoming an environmental expert! Keep shining, and let’s keep pushing forward!
