TOPIC: AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS
CONTENT
Benzene, structure, properties and Uses
Derivative of Benzene
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
These are hydrocarbons that have the same structure as benzene.
Benzene: Benzene is a typical aromatic compound with molecular formula of C6H6. It has the structure of:
Preparation:-
- From coal tar: The destructive distillation of coal produced coal tar which contain benzene
- From petroleum; The dehydrogenated of alkane using valladim(v)oxide (v2O5) as catalyst at 500oC and 20 atmos give benzene
C6H14 V2O2 C6H6 + 4H2
The process is known as catalytic reforming.
- From polymerization of ethyne
3 ( H – C = C – H ) C6H6
Evaluation
- Describe three (3) ways of preparing benzene.
- Draw the structure of benzene.
Physical properties
- It has a pleasant odour.
- It has boiling point of 80oC.
- Benzene can dissolve in water.
- It burns with sooty flame.
Chemical Properties
Benzene can undergo both additional reaction and substitutional reaction.
- Additional Reaction.
- Hydrogenaton: Benzene reduces to cyclo-hexane if hydrogen gas is passed through finely divided nickel at 150oC.
- Halogenation: In the presence of ultra-violet light, benzene reacts with halogen to produce cyclic compound.
C6H6 + 3 Cl2 UV
Light
- Substitution Reaction.
- Benzene undergoes substitution reaction due to the presence of its single bonds.
- Halogenation e.g. Cl2, Br2, I2
+ Br2
Benzene Bromobenzene
- Nitration: This occurs in the mixture of HNO3 and H2SO4 together with benzene
HNO3 Nitrobenzene.
iii. Sulphonation: Benzene reacts with conc., H2SO4 to form benzene sulphonic acid.
- Alkylation: It involves reactions of benzene with halo-alkanes in the presence of AlCl3.
Uses.
- It is used as a solvent to dissolve organic.
- It is used as fuel in petrol.
- It is used in the manufacture of aromatic compound e.g. benzoic acid.
Evaluation
- State two (2) uses of benzene
- Identify two (2) chemical properties of benzene with examples.
Derivatives of Benzene
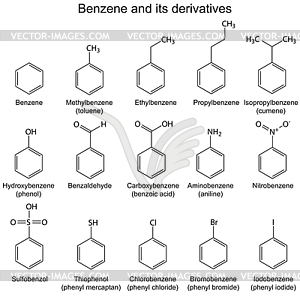
Evaluation
- Give another name to the following compounds
(a ) Phenol (b) Toluene
- State four (4) derivatives of benzene.
READING ASSIGNMENT
New School Chemistry By .O.Y. Ababio, pg 492-494.
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
- Benzene can be prepared from the following except
(a) Coal tar (b) petroleum (c) Alkanol (d) Ethyne
- Benzene can undergo additional reaction due to presence of
(a) double bonds (b) single bonds ( c) hydrogen ( d) carbon.
- Benzene undergoes the following reaction except.
(a) substitution (b) addiction (c) Hydrogenation ( d) polymerization
- The technique used in separating a mixture of common salt and water is
(a) evaporation (b) sublimation (c) decantation (d) chromatography.
Theory
- a. State two (2) uses of Benzene
- identify two (2) physical properties of benzene.
- a. How would you prepare benzene?
- State two (2) chemical properties of benzene.
