Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, my brilliant friend! I hope you’re having a fantastic day! Have you ever peeled the bark of a tree and noticed the soft, cork-like layer underneath? Or wondered how trees protect themselves from injuries and harsh weather? The answer lies in a special tissue called the cork cambium, also known as phellogen.
Today, we’ll learn about cork cambium and phellogen activity, how they help plants grow, and why they are essential for survival.
Cork cambium and phellogen activity
What is Cork Cambium (Phellogen)?
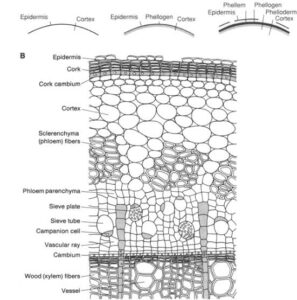
The cork cambium, or phellogen, is a type of secondary meristem that produces protective tissues in woody plants. It is part of the periderm, which replaces the epidermis as the plant grows older.
The periderm consists of:
Phellogen (Cork Cambium) – The thin layer of meristematic cells that divides actively.
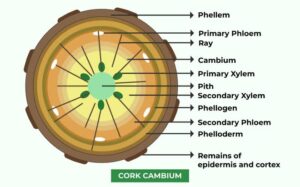
Phellem (Cork) – The outer protective layer made of dead, waterproof cells.
Phelloderm – The inner living tissue that provides nutrients.
How Does Phellogen Activity Work?
Phellogen develops from living cells in the cortex (outer stem tissue).
It divides to produce cells in two directions:
Outward → Forms cork (phellem), which is dead and waterproof.
Inward → Forms phelloderm, which is living and provides nutrients.
As more cork is produced, older layers become part of the bark, providing protection.
Functions of Cork Cambium and Phellogen Activity
Protects the plant from physical damage, pathogens, and extreme temperatures.
Prevents water loss by producing suberin, a waxy substance in cork cells.
Allows gas exchange through small openings called lenticels.
Aids secondary growth, allowing stems to expand as the plant matures.
A Simple Story to Understand Cork Cambium
Imagine you have a favourite school notebook. Over time, the cover gets worn out, so you wrap it with a stronger protective cover to keep it safe. Trees do the same thing! Their original outer layer (epidermis) wears out, so the cork cambium produces a tougher bark to protect the tree.
Summary
Cork cambium (phellogen) is a secondary meristem that produces cork (phellem) and phelloderm.
Phellem (cork) is dead and protects the plant from water loss and infections.
Phelloderm is living and provides nutrients.
Phellogen activity helps trees grow, form bark, and survive in harsh conditions.
Evaluation
- What is another name for cork cambium?
- What are the three layers of the periderm?
- Why is cork waterproof?
- What is the function of lenticels?
- How does cork cambium help plants survive?
You are doing an amazing job! You are learning the secrets of how trees protect themselves and grow strong! The next time you see tree bark, remember the amazing work of the cork cambium. Keep learning with Afrilearn, and I’ll see you in the next exciting lesson. Stay curious and keep growing!
