Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, my brilliant friend! I hope you’re having a great day! Have you ever wondered what gives plants their shape? Why do plants stand firm even when the wind blows? Or how water and nutrients move from one cell to another inside a plant? These amazing abilities are possible because of three important structures in plant cells—the cell wall, plasmodesmata, and vacuoles.
Think of a school building. The walls give it shape and strength, the doors allow movement between rooms, and the storage cupboards keep extra books and supplies. In the same way, the cell wall provides structure, plasmodesmata connect cells for communication, and vacuoles store important substances. Let’s look at each of these structures in detail!
Structure and function of cell wall, plasmodesmata, and vacuoles
Cell Wall – The Protective Shield
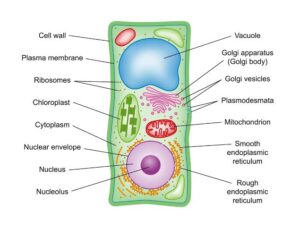
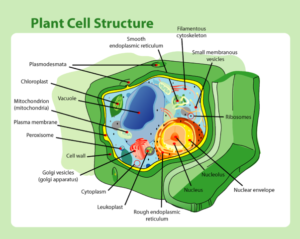
The cell wall is a tough, rigid layer that surrounds plant cells. Unlike animal cells, which have only a thin membrane, plant cells have this extra protection. It acts like the fence around a compound, giving the plant cell strength and support.
Functions of the Cell Wall:
Provides Strength and Support: Just like concrete walls hold up a house, the cell wall helps plants stay upright, even tall trees like iroko and baobab.
Prevents Bursting: When plants absorb too much water, the cell wall stops the cell from bursting, just like how a strong water tank holds water without breaking.
Allows Water and Nutrients to Pass Through: The cell wall is not completely solid—it has tiny holes (pores) that let water and minerals pass between cells, ensuring every part of the plant gets what it needs.
Plasmodesmata – The Communication Channels
Now, imagine that every classroom in a school had no doors or windows—students wouldn’t be able to move between rooms or pass information! In plant cells, plasmodesmata act as tiny doorways between neighbouring cells, allowing movement and communication.
Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels that connect plant cells. They are like secret passageways that allow cells to share water, nutrients, and chemical signals.
Functions of Plasmodesmata:
Allows Cells to Share Resources: Just like people in a family share food, plasmodesmata help cells share water, sugars, and nutrients.
Helps in Cell Communication: These channels allow cells to send signals to each other, ensuring that all parts of the plant work together.
Supports Plant Growth: Since cells communicate through plasmodesmata, plants can coordinate growth and respond to changes in their environment.
Vacuoles – The Plant’s Storage Unit
Have you ever seen a water reservoir in your neighbourhood? It stores water so that people can use it when needed. In plant cells, vacuoles act like storage tanks, holding water, food, and waste products.
A vacuole is a large, fluid-filled sac found in the centre of most plant cells. It contains water, minerals, and sometimes waste products that the plant doesn’t need immediately.
Functions of Vacuoles:
Stores Water and Nutrients: The vacuole holds water and essential nutrients for the cell’s survival. In dry conditions, plants rely on the water stored in vacuoles.
Maintains Cell Shape and Firmness: When a vacuole is full, it pushes against the cell wall, making the cell firm. This is why well-watered plants stand upright, but dry plants wilt.
Helps in Waste Disposal: Just like humans need to remove waste, plant cells store unwanted substances in vacuoles before safely getting rid of them.
A Simple Story to Understand These Structures
Imagine you are building a small farm hut. You make strong walls to give it shape (just like a cell wall). You add doors so people can move between rooms (like plasmodesmata), and finally, you include storage containers for water and food (like vacuoles). Each part plays a key role in keeping your hut functional, just as these structures keep plant cells strong and efficient!
Summary
The cell wall provides strength, protection, and support to plant cells.
Plasmodesmata are small channels that connect plant cells, allowing communication and the sharing of nutrients.
The vacuole stores water, nutrients, and waste, and helps maintain the plant’s shape.
Together, these structures ensure that plants grow well, stay strong, and survive in different conditions.
Evaluation
- What is the main function of the cell wall in plant cells?
- How do plasmodesmata help plant cells communicate?
- Why do vacuoles play an important role in plant survival?
- What happens to a plant when its vacuoles lose water?
- Give an example of how the cell wall, plasmodesmata, and vacuole work together in a plant.
You are doing an amazing job! Every lesson you complete brings you one step closer to becoming an expert in plant biology! Keep going, stay curious, and never stop asking questions. I’m so proud of you, and I can’t wait for our next exciting lesson together. Keep learning with Afrilearn—see you soon!
