Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, my dear Afrilearn scholar! I hope you are doing great today! I know you are eager to learn, and that makes me really proud of you. Today, we are about to understand something very interesting—Plant Ecology! Don’t worry; I will make it so simple and relatable that you will never forget it.
Definition and scope of plant ecology
Imagine this: You walk into a forest, and you see trees, grasses, shrubs, and even tiny mosses covering the rocks. Birds are chirping, insects are buzzing, and somewhere in the distance, a monkey is jumping from one tree to another. All these living things depend on each other to survive. This relationship, my dear scholar, is what plant ecology is all about!

Plant ecology is the branch of botany that studies how plants interact with each other, with animals, and with their surroundings. Just as we humans live in communities, plants also form communities where they help, compete, and sometimes even fight for survival
To fully understand plant ecology, we must look at its scope—that is, what it covers. Plant ecology does not just focus on trees, shrubs, and grasses; it also studies the soils they grow in, the air they breathe, and even the tiny organisms that live around them. It helps us answer questions like:
How do plants survive in harsh deserts, where there is almost no water?
Why do we have tall, thick forests in the south of Nigeria but short grasses in the north?
What happens to plants when human activities like farming and deforestation disturb their environment?
Plant ecology covers many aspects, but let’s summarise some key areas:
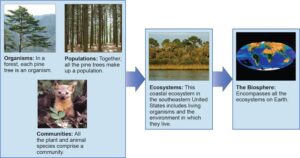
Plant Communities – Just like we live in families, plants also live in groups. Some trees grow together in forests, while grasses form savannas. Each plant community has its own special way of surviving.
Plant-Environment Interaction – Plants do not live in isolation. They depend on sunlight, water, air, and soil to grow. Some plants love wet areas (like the water lily), while others prefer dry land (like the cactus).
Competition and Cooperation – Plants compete for sunlight, space, and nutrients. A big tree with large leaves may block the sunlight from smaller plants, but at the same time, it can protect them from heavy rain and wind.
Human Impact on Plant Life – Human activities such as farming, deforestation, and urbanisation affect plant ecology. For example, when we cut down trees, we destroy plant communities and disturb the balance of nature.
Summary
Plant ecology is the study of how plants interact with their environment and with other living things. It helps us understand plant communities, their relationships, and how they survive in different conditions. This knowledge is very important, especially in protecting our natural environment and ensuring that plants continue to thrive
Evaluation
- What is plant ecology?
- Mention three things plant ecology studies.
- Give an example of a plant that thrives in dry areas and one that thrives in wet areas.
- How do human activities affect plant ecology?
You are doing so well! Always remember that plants are life; they provide us with food, medicine, and even the air we breathe. Keep learning with Afrilearn, and I promise you, success is just around the corner. See you in the next lesson!
