Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, Afrilearn Scholar! I hope you’re having a fantastic day and feeling ready for our exciting lesson today! We’re going to explore something that is fundamental to understanding plant ecology—identifying plant species and understanding their ecological roles. Whether you’re in a forest, grassland, or even your own backyard, every plant species you encounter plays a unique part in the ecosystem. By the end of this lesson, you’ll not only be able to identify different plant species but also understand their important functions in nature. Let’s get started!
Identifying plant species and their ecological roles
What is Plant Identification?
Plant identification is the process of recognizing and naming different species of plants based on their physical characteristics such as leaf shape, flower structure, bark type, and other traits. It’s like learning to recognise friends by their faces—each plant has its own unique features!
In Nigeria, you might come across all sorts of plants, from the mango tree to the baobab tree, each with distinct characteristics that help you identify them. But identification is more than just recognising plants; it’s also about understanding what role each plant plays in its ecosystem.
Why is Identifying Plants Important?
Ecological Understanding: When you know the species in a given area, you can understand how they interact with each other and the environment. Are they helping to improve soil quality? Are they food for certain animals? Are they providing shelter for insects or birds?
Conservation: Identifying plant species is vital for conservation efforts. By knowing which plants are endangered or have medicinal value, you can help protect them or use them sustainably. For instance, many Nigerian plants are used in traditional medicine, and knowing them helps in their conservation.
Agriculture: In farming, understanding which plants are beneficial or harmful (like invasive species) can improve crop yields and soil health. For example, legumes like cowpea (a Nigerian favourite) can fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting surrounding crops.
Cultural Significance: Plants are deeply embedded in Nigerian culture and daily life, from yam vines used in farming to shea trees for their butter. Identifying plants helps preserve traditions and understand their value to communities.
How to Identify Plant Species
There are several key features you can look at to identify plant species. Let’s break them down:
Leaves can vary greatly in shape, size, and arrangement. For example, cassava has large, palmate leaves, while the coconut tree has long, narrow leaves. The arrangement of leaves on the stem—whether opposite, alternate, or whorled—also helps in identification.
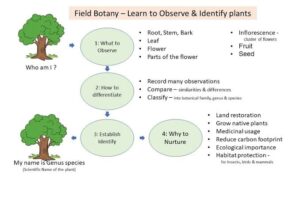
Flowers: The structure of the flowers, such as the colour, shape, size, and arrangement, is another key feature for identification. Think about the beautiful African tulip tree, with its bright orange flowers, or the hibiscus, which is a common sight in Nigerian gardens.
Bark: The texture, colour, and pattern of a tree’s bark can also help identify it. For instance, the baobab tree has a distinctive, smooth, grey bark, while the iroko tree has rough, dark bark.
Fruit: The fruit of a plant is another key identifier. For example, the mango tree is easy to identify by its large, sweet fruit, while guava trees have small, round fruits that turn yellow or green when ripe.
Size and Shape: The overall size of the plant and its shape—whether it’s a small shrub, a tall tree, or a creeping vine—can also provide clues. Palm trees are easily identifiable by their tall, slender trunks and large leaves at the top.
Ecological Roles of Plants
Once you’ve identified a plant, the next step is to understand the important ecological roles it plays. Each plant contributes to the health of the environment in different ways. Let’s look at a few examples:
Producers in the Food Chain: Plants are producers in the food chain, meaning they use sunlight to make food through photosynthesis. Without plants, there would be no primary source of food for herbivores (and, of course, carnivores depend on herbivores for food). For example, grass in the savannah serves as food for herbivores like antelope and zebras.
Supporting Biodiversity: Plants provide habitat and food for animals, insects, and microorganisms. For instance, the mango tree supports various species, including birds that feed on its fruits and insects that pollinate its flowers. Mangroves along Nigeria’s coastline provide shelter for fish and other marine life.
Soil Formation and Protection: Plants, especially trees, help with soil conservation. Their roots hold the soil together, preventing erosion. The cashew tree, for example, helps protect the soil in areas prone to erosion, like parts of Ondo and Ogun states.
Nutrient Cycling: Plants help cycle nutrients in the soil. When they die, they decompose and release organic matter back into the soil, enriching it with nutrients for future plant growth. Legumes, like cowpea, help fix nitrogen in the soil, improving soil fertility for other crops.

Water Regulation: Plants play a key role in the water cycle. Through transpiration, they release water vapour into the atmosphere, helping to regulate local climates. Trees like the giant bamboo in Nigeria can help maintain local water cycles, ensuring that rainfall is evenly distributed.
Examples of Nigerian Plant Species and Their Ecological Roles
Mango (Mangifera indica): The mango tree is not only important for its delicious fruit but also for its role in supporting local wildlife. Birds, monkeys, and insects rely on its fruit and flowers, while its roots help prevent soil erosion.
Baobab (Adansonia digitata): This iconic tree provides shelter and food for animals. Its fruit is rich in vitamin C and is consumed by both humans and animals. Baobabs also store large amounts of water in their trunks, which is vital in dry regions.
Cassava (Manihot esculenta): While primarily a crop, cassava also plays a role in improving soil fertility. Its roots provide food for humans, and its leaves are used for fodder in some parts of Nigeria.
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor): Sorghum is a drought-tolerant crop that helps sustain food security in regions with unpredictable rainfall. It also helps prevent soil erosion by binding the soil with its roots.
Summary
In today’s lesson, we’ve learned about the importance of identifying plant species and understanding their ecological roles. By knowing how to identify plants—whether by their leaves, flowers, fruit, or bark—you can better understand their role in the environment. Whether they are producers, habitats for animals, or contributors to the water and nutrient cycles, plants play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance.
Evaluation
- Why is it important to identify plant species in an ecosystem?
- What are some key features used to identify plants in the field?
- How do plants contribute to the water cycle?
- How does the mango tree play a role in supporting local wildlife?
- Explain the role of legumes in improving soil fertility.
Well done, Afrilearn scholar! You’ve done an amazing job learning how to identify plants and understanding the vital roles they play in the environment. This knowledge will help you not only in your studies but also in understanding the world around you. I’m so proud of your progress, and I can’t wait for the next lesson! Keep up the great work!
