Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, my smart Afrilearn scholar! I hope you’re having a fantastic day! Have you ever wondered why some plants grow tall and strong while others stay small and weak? Or why some plants only flower at certain times of the year? Well, my dear scholar, it all comes down to light and photoperiodism! Today, we’re going to break it down in a fun and simple way that will stick with you forever.
Light and photoperiodism in plant growth
Imagine you plant two seedlings—one under bright sunlight and the other in a dark room. After a few weeks, the one in the sunlight grows strong and green, while the one in the dark looks weak and pale. Why? Because plants need light to survive!
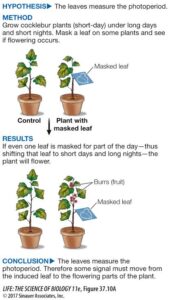
Light and Its Role in Plant Growth
Light is one of the most important factors that influence plant growth. Plants use light for photosynthesis, the process where they make their own food. Without light, plants cannot produce energy, and they eventually die.
Light affects plant growth in three main ways:
Light Intensity (Brightness of Light) – This determines how much energy a plant gets. A plant in a shady area may not grow as well as one in direct sunlight. That’s why crops like tomatoes need bright sunlight, while ferns grow well in low light.
Light Duration (Photoperiod) – This refers to how long a plant is exposed to light each day. Some plants need long hours of sunlight to flower, while others require shorter periods.
Light Quality (Type of Light) – Plants mainly use red and blue light for photosynthesis. That’s why they grow better under natural sunlight than artificial yellow light.
Photoperiodism: How Plants Respond to Light Duration
Now, let’s talk about photoperiodism—a big word that simply means how plants respond to the length of day and night. Just like humans have body clocks that tell us when to wake up or sleep, plants also have internal clocks that control their growth and flowering based on the length of daylight.
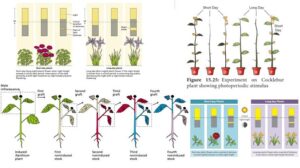
Plants are grouped into three categories based on their photoperiodic response:
Short-Day Plants (SDP) – These plants flower when nights are longer than a certain number of hours. Examples include yam, sorghum, and millet, which flower during Nigeria’s dry season when nights are longer.
Long-Day Plants (LDP) – These plants need long hours of daylight to flower. Examples include lettuce and spinach, which thrive during the long daylight periods of the rainy season.
Day-Neutral Plants (DNP) – These plants are not affected by day length. They flower whenever they are mature, regardless of light duration. Examples include tomatoes and maize.
Summary
Light is essential for plant growth, as it helps in photosynthesis. The intensity, duration, and quality of light affect how plants grow. Photoperiodism is how plants respond to the length of daylight, which influences their flowering. Plants are classified into short-day plants, long-day plants, and day-neutral plants based on how they react to light duration.
Evaluation
- Why is light important for plants?
- What are the three main ways light affects plant growth?
- Define photoperiodism and give an example of a short-day plant.
- How do long-day plants differ from short-day plants?
You are amazing! Keep learning and shining bright like the sun that helps plants grow. Who knows? One day, you might use this knowledge to improve farming in Nigeria and beyond! Keep going with Afrilearn, and see you in the next lesson!
