Back to: BASIC TECHNOLOGY JSS3
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about motion engineering. Enjoy the class!
Motion Engineering Projects
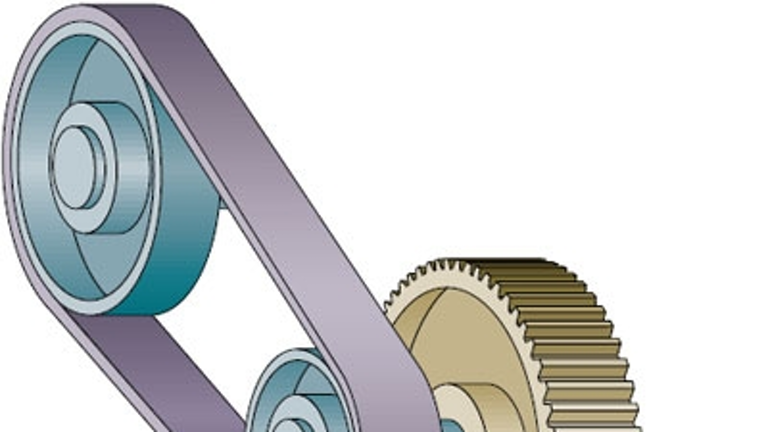
Motion can be defined as the movement of a body (object) from one point to another with the application of force.
Types of motion in motion engineering
- Linear Motion: This is the motion of a body moving in a straight line. For instance, a push-pull link mechanism is a simple machine that operates with linear motion.
- Rotary Motion: This is the motion of a body moving in a circular form.
Examples of circular motion are the rotation of a fan, vehicle tyres, the handle of the clock, etc.
- Reciprocating Motion: This is a linear motion that reverses direction periodically.
- Oscillations: This is a rotary motion that reverses or changes direction periodically. An example is the motion of a pendulum bob in clocks.
- Irregular Motion: This is the type of motion that randomly changes direction. For instance, smoke particles have irregular motion.
Rotary motion
Rotary Motion is the motion of a body moving in a circular form. Examples of circular motion are the rotation of a fan, vehicle tyres, the handle of the clock, etc.
Types of rotary motion
(i) One-way rotary motion: This is the type of motion that is strictly clockwise or strictly anti-clockwise. In a one-way rotary motion, a reversal of direction can lead to damage to such a machine.
Examples of one-way rotary motion include driving shaft of an automobile, electric fan, circular sawing machine, etc.

(ii) Reversible rotary motion: This is the type of rotary motion that can go clockwise and anti-clockwise. For example, in vehicles, reversible rotary motion makes it possible for a car to reverse and go backwards. A crane also has a reversible rotary motion to be able to lift and drop loads in its load drum.
E.g. Function of the Clutch: The function of the clutch is to disconnect two shafts running at different speeds, that is, the engine crankshaft and the gearbox shaft.
Types of Car Engines
- Front- Engine Rear-Wheel Drive: This is an engine that consists of a clutch, a gearbox, a propeller shaft and a rear axle. Most cars in Nigeria operate with this type of engine.
- Front-Engine Front Wheel Drive: In this type of engine, every other part mentioned in Front- Engine Rear-Wheel Drive is present except for the propeller shaft. Transmission is directly from the gearbox to the rotating wheels.
- Rear-Engine Rear-Wheel Drive: In this type of engine, there is no propeller shaft also. The clutch, engine and gearbox are all engineered at the back of the car. An example is Volkswagen cars.
- Front-Engine 4-Wheel Drive: This is a more recent technological advancement in the engineering of cars. There is no propeller shaft and most times no mechanical gearbox. The gear system is a hydraulic system. This car contains the brake and the accelerator only, with all four wheels connected to the gearbox.
Control of rotary motion-brakes
Brakes are meant to control motion. The kinetic energy in a moving object is absorbed by the brake. This produces heat on the brake as kinetic energy is converted into potential energy. As the brake absorbs heat, the vehicle slows down until it finally comes to a stop.
How brakes work
There are different types of brakes. However, the principle of how the brake works is the use of friction. If the brake in a car or bicycle is pressed against the rotating drum or disc or wheel, the resulting friction between the pad and the drum or wheel slows down the rotating wheels, until they eventually come to a stop.
Conversion of rotary motion to linear motion
(i) Sewing Machine: In some machines, it is necessary for a change from one form of the motion to another along its line of operation.
For instance, a sewing machine will need to convert linear motion from the moving pedal to rotary motion at the wheel and finally to linear motion again at the needle.
(ii) Piston-Crank mechanism of a car engine is another example of converting rotary motion at one point of an engine to rotary motion at another point of the same engine.
(iii) Crank and Slider: The crank and slider mechanism is used in certain machines. The mechanism consists of a rotating crank which rotates about its centre and an arrangement of levers which acts as a linkage to a sliding block constrained to execute linear motion at the other end. In an automobile, this system is described as the piston and crankshaft.
So, in a machine, the crank and slider device can work in changing rotary motion to linear motion or from linear motion into rotary motion.
Other examples of machines involved in converting one form of energy to another are; Screw jack, Rack and piston steering system, Crankshaft and cylinder, Metalwork table vice, Woodworker’s vice, Pipe vice, G-clamp, etc
In our next class, we will be talking about SIMPLE ELECTRICAL WIRING. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

God bless you all. I love your approach to teaching Basic Keep up the good job.
I searched for TD lessons in your ng, l didn’t see it. Work on it please.
Thanks
I need more examples of conversion of rotary motion to linear motion
Noted.
what is the meaning of electrical wiring