Back to: AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE SS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking more about reproduction in farm animals. Enjoy the class!
Reproduction in Farm Animals II

CONTENT:
- Processes of egg formation in poultry
- Male and female reproductive hormones
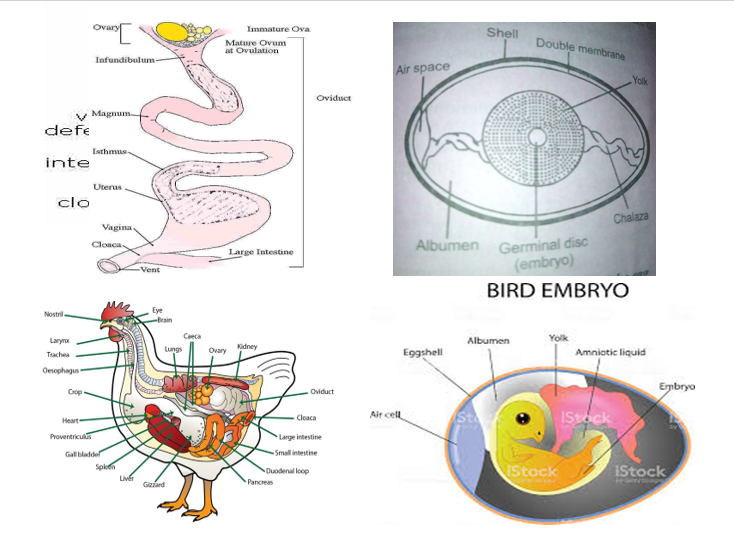
Processes of egg formation in poultry
The egg in poultry is partly formed in the ovary and the oviduct. At ovulation, the ovum carrying the yolk is released by the ovary into the oviduct through the funnel called the infundibulum. Fertilization takes place in the infundibulum where the egg spends 15 minutes and moves into the magnum. In the magnum, part of the egg white (albumen) and the chalaza are secreted around the yolk. The egg stays for 3 hours in the magnum and moves into the isthmus where the two shell membranes are formed. The egg stays for 1 hour 15 minutes in the isthmus and moves into the uterus where it remains for 18 – 21 hours and the eggshell is formed from calcium carbonate. Mineral solutions are also added to the egg before it moves into the vagina where it remains for 1 – 15 minutes before it is laid through the cloaca. A complete formation of eggs takes almost 26 hours.
Evaluation
- Describe the processes of egg formation in poultry.
- Describe the reproductive system of poultry birds.
Male and female reproductive hormones:
Hormones are organic chemical substances produced by endocrine (ductless) glands which influence growth, development and metabolic activities in farm animals. These include
| HORMONE | SEX | SITE OF SECRETION | FUNCTIONS |
| Testosterone/ Androgen | Male | Testes | It stimulates the development of secondary sexual characters in male. It stimulates sperm production through spermatogenesis. |
| Oestrogen | Female | Ovary | It stimulates the development of secondary sexual characteristics in female animals It promotes the production of ova or eggs through oogenesis. It stimulates mammary gland development |
| Progesterone | Female | Corpus luteum | It ensures uterus development and implantation of the fertilized ovum. It inhibits oestrus i. e. prevents ovulation. It stimulates the development of the mammary gland It ensures the continuance of pregnancy. |
| Oxytocin | Female | Pituitary | It aids the contraction of the uterine wall during parturition. It promotes milk let-down after parturition. It aids sperm transportation in the vagina. |
| Relaxin | Female | Pituitary | It aids relaxation of pelvic ligaments during parturition. |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Female | Pituitary | It stimulates the growth of the ovarian follicle.
|
| Luteinizing hormone | Female | Pituitary | It stimulates the secretion of oestrogen and progesterone. It causes the rupture of the follicle and the release of the ova from the follicle. |
General evaluation
- List five animal hormones and function.
- What are the functions of the following in the processes of egg formation in poultry?
- Ovary
- Oviduct
- Magnum
- uterus
Reading assignment
- Essential Agricultural Science for Senior Secondary Schools by O.A. Iwena chapter 30 page 288 – 290.
- Answer the following questions from WAEC PAQ 2015 theory question 4a
Theory
- Draw and label the diagram of an egg.
- List five reproductive hormones, site of secretion and their functions.
In our next class, we will be talking about Environmental Physiology. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
