Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, my brilliant friend! I hope you’re doing great today! Have you ever wondered how a tiny seed grows into a big tree? Or how plants keep producing new leaves, roots, and flowers? It all happens because of something special called meristems!
Meristems are like the “engine rooms” of plants—they contain cells that continuously divide, helping plants grow, repair damage, and develop new structures. Today, we’ll talk about the role of meristems in plant development and why they are so important.
Role of meristems in plant development
What are Meristems?
Meristems are regions in a plant where cells are constantly dividing. These cells are undifferentiated, meaning they haven’t yet developed into specific plant tissues. Think of them like baby cells that can grow into different parts of the plant, just like stem cells in humans!
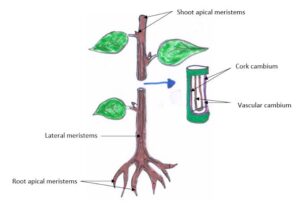
There are three main types of meristems:
Apical meristems – Found at the tips of roots and shoots, responsible for making plants taller.
Lateral meristems – Found along the sides of stems and roots, making plants thicker.
Intercalary meristems – Found in grasses and some fast-growing plants, helping them regrow quickly after being cut.
Roles of Meristems in Plant Development
1. Growth – Making Plants Taller and Thicker
Meristems help plants grow in two ways:
Apical meristems allow plants to grow taller and their roots to grow deeper into the soil.
Lateral meristems make plant stems and roots wider and stronger, which is why tree trunks get thicker over time.
Imagine a house under construction—workers keep adding bricks (new cells) to make the building taller (apical meristems) and wider (lateral meristems).
2. Formation of Different Plant Tissues
The dividing cells in meristems eventually develop into specialised plant tissues like:
Xylem – Transports water from roots to leaves
Phloem – Carries food (sugar) from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Epidermis – Forms the outer covering of the plant for protection.
It’s like a school where students (meristematic cells) grow and take on different roles—some become doctors (xylem), some become teachers (phloem), and some become security guards (epidermis)!
3. Wound Healing and Regeneration
Ever seen a plant heal itself after getting cut or damaged? That’s because of meristems! When a plant is injured, meristematic cells quickly divide to replace damaged tissues and allow new growth.
This is why a pruned hibiscus plant grows back beautifully or why a tree can still sprout new shoots even after being cut.
4. Production of Flowers and Fruits
Meristems also help plants produce flowers, fruits, and seeds, ensuring reproduction. When a plant reaches maturity, its meristems produce flower buds, which later develop into fruits. Without meristems, plants wouldn’t be able to reproduce!
Think about a tomato plant—its apical meristem helps it grow taller, while special meristems in the flower buds help it produce tomatoes.
5. Adaptation to the Environment
Meristems help plants adapt to their surroundings by responding to different conditions:
If a tree is cut down, new shoots can grow from lateral meristems.
If a plant is constantly grazed by animals (like grasses in a field), intercalary meristems ensure it keeps growing back.
If roots need to reach deeper for water, apical meristems make them grow longer
Meristems are like a plant’s survival strategy, helping it adjust and thrive no matter what happens!
A Simple Story to Understand the Role of Meristems
Imagine you are building a house:
Apical meristems add more floors, making the house taller.
Lateral meristems make the walls thicker, making it stronger.
Intercalary meristems help repair any damage quickly.
Just like a house grows and develops with time, meristems ensure plants keep growing and adapting!
Summary
Meristems play a crucial role in plant development by:
Helping plants grow taller (apical meristems) and wider (lateral meristems).
Producing new plant tissues like xylem and phloem.
Assisting in wound healing and regeneration.
Enabling the formation of flowers, fruits, and seeds for reproduction.
Allowing plants to adapt to different environmental conditions.
Without meristems, plants wouldn’t be able to grow, repair themselves, or reproduce!
Evaluation
- What are the three types of meristems in plants?
- How do apical meristems help a plant grow?
- What is the role of lateral meristems in trees?
- Why are meristems important for wound healing in plants?
- How do meristems help plants adapt to their environment?
You are doing an amazing job! Wow! You’re learning so much about how plants grow and survive. Keep paying attention to the plants around you—you’ll start seeing how meristems work in real life. Keep learning with Afrilearn, and I’ll see you in the next exciting lesson. Stay curious and keep growing!
