Back to: Computer Science Primary 2
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we’re venturing into the inner workings of a computer’s system unit to explore a crucial component: the disk drive. The disk drive is like the computer’s personal librarian, storing and retrieving data for your digital adventures.
System Unit – Disk drive
A disk drive is a fundamental component within the system unit responsible for data storage and retrieval.
1. Types of Disk Drives:
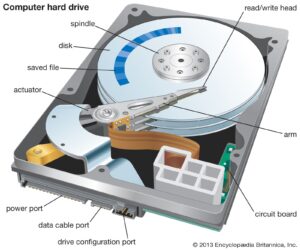
Disk drives come in different types, including hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). HDDs use spinning disks for storage, while SSDs rely on flash memory.
Both types of drives store data, but SSDs are faster and more durable, while HDDs offer larger storage capacities at a lower cost.
Disk drives are used to store the computer’s operating system, software applications, documents, photos, videos, and more.
2. Data Retrieval and Storage:

The disk drive reads and writes data to and from storage media, such as magnetic disks in HDDs or NAND flash memory in SSDs.
It retrieves data when you open files or run programs and stores data when you save files or install software.
Disk drives play a crucial role in data access, ensuring that the computer can read and write data efficiently.
3. Disk Drive Interfaces:
Disk drives connect to the computer’s motherboard through various interfaces, including SATA (for HDDs and SSDs), M.2 (for SSDs), and NVMe (for high-speed SSDs).
The interface determines the speed and compatibility of the disk drive with the computer.
Different interfaces cater to a range of computer systems, from traditional desktops to ultrabooks.
4. Capacity and Performance:
Disk drives come in different storage capacities, ranging from gigabytes (GB) to terabytes (TB), with SSDs offering additional speed advantages.
The drive’s capacity determines how much data it can store, while its type affects data access speed.
Users choose disk drives with suitable capacity and performance based on their storage needs and usage.
5. Disk Management and File Systems:
Disk drives are managed by the computer’s operating system and use specific file systems (e.g., NTFS, FAT32) to organize and retrieve data.
The file system helps keep data organized and accessible, while disk management tools allow users to format and partition drives.
Disk management ensures data integrity and helps users keep their data organized and secure.
Disk drives have come a long way from their early days of floppy disks. Today’s disk drives store massive amounts of data and deliver it at lightning speed.
In conclusion, the disk drive is a pivotal component within a computer’s system unit, responsible for data storage, retrieval, and management. The choice between HDDs and SSDs, along with considerations of capacity and performance, depends on the user’s specific needs. Understanding the disk drive is essential for efficient data management in the digital age!
Question Time:
- What are the two main types of disk drives commonly used in computers, and how do HDDs and SSDs differ in terms of their technology and functionality?
- How does a disk drive facilitate data retrieval and storage in a computer, and what is its role in ensuring data access and data-saving processes?
- What are the various interfaces used for connecting disk drives to a computer’s motherboard, and how do these interfaces impact the drive’s speed and compatibility?
We have come to the end of today’s class. I hope you enjoyed the class!
In the next class, we shall be discussing how to Draw and Label the System Unit.
In case you require further assistance or have any questions, feel free to ask in the comment section below, and trust us to respond as soon as possible. Cheers!

