Back to: Botany 300 Level
Hello, my bright Afrilearn scholar! I hope you’re feeling inspired today because we’re about to embark on a journey to explore vegetation types and their ecological significance! Have you ever noticed how the plants in one area are different from those in another area? Whether it’s the lush greenery of the rainforest or the dry, sparse grasses of the savanna, each vegetation type plays a vital role in maintaining the balance of life on Earth. Today, we’re going to understand the types of vegetation we find in different parts of the world and how each one contributes to the health of our planet.
Vegetation types and their ecological significance
What Are Vegetation Types?
Vegetation refers to the types of plants that grow in a particular area. These plants are determined by various factors such as climate, soil, water, and temperature. The different vegetation types around the world have their own characteristics, which means they are adapted to specific conditions.
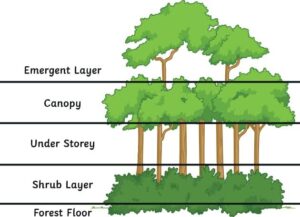
The main types of vegetation include:
Forest Vegetation
Grassland Vegetation
Desert Vegetation
Wetland Vegetation
Let’s break these down to understand them better and see how each plays an important role in the environment!
1. Forest Vegetation: The Lungs of the Earth
Forests are dense areas filled with trees, shrubs, and other plant life. They are found in areas with high rainfall and warm temperatures, such as in Nigeria’s tropical rainforest zone. There are different types of forests, including tropical rainforests, temperate forests, and boreal forests.
Ecological Significance of Forest Vegetation
Biodiversity – Forests are home to millions of species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, making them biodiversity hotspots.
Carbon Sink – Forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to regulate the Earth’s climate by reducing greenhouse gases.
Water Cycle Regulation – Forests play a key role in the water cycle by maintaining moisture and controlling rainfall patterns.
Soil Protection – The roots of trees prevent soil erosion and help maintain soil fertility.
Example:
The Cross River Rainforest in Nigeria is an example of forest vegetation that supports rare species like the Cross River gorilla, and it plays a huge role in climate control and water regulation.
2. Grassland Vegetation: The Heart of the Savannah
Grasslands are vast, open areas dominated by grasses and occasional scattered trees. They are found in regions with seasonal rainfall, where there’s not enough water to support forests but more than enough for grasses to thrive. Grasslands are common in places like the savannas of West Africa and parts of Nigeria’s middle belt.
Ecological Significance of Grassland Vegetation
Grazing Land – Grasslands are critical habitats for grazing animals such as antelope, buffalo, and cattle, which support the livelihoods of millions of people.
Carbon Sequestration – Grasslands store large amounts of carbon in their roots and soil, helping to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Soil Fertility – The decaying grasses add nutrients to the soil, which is essential for crop production.
Support for Pollinators – Many grasslands are home to bees, butterflies, and other pollinators that help with the reproduction of plants.
Example:
In Nigeria’s Sokoto Plains, the grasslands support the nomadic Fulani herders who rely on the land to graze their cattle. These grasslands are also important for wildlife conservation.
3. Desert Vegetation: Adaptations to Dryness
Deserts are dry, barren landscapes that receive very little rainfall, usually less than 250mm annually. Cacti, succulents, and hardy shrubs dominate desert vegetation, which can be found in places like the Sahara Desert and the Kalahari. In Nigeria, the northern parts of the country experience semi-desert conditions.
Ecological Significance of Desert Vegetation
Water Conservation – Desert plants are highly adapted to conserve water. They have thick, waxy cuticles and deep roots to survive in extreme heat.
Biodiversity – Despite the dry conditions, deserts host unique species of plants and animals, including cactus plants and desert tortoises, which are specially adapted to harsh climates.
Soil Stabilisation – Plants like cacti have deep roots that help hold the soil together and prevent sandstorms.
Medicinal Value – Many desert plants have medicinal properties, and traditional medicine relies on them.
Example:
The Cactus plants found in the Sahara Desert have adapted to store water in their stems, helping them survive the hot and dry conditions.
4. Wetland Vegetation: The Water Lovers
Wetlands are areas where water saturates the soil for most of the year. These include swamps, marshes, and bogs. Wetlands are found in areas with high rainfall or near bodies of water like rivers or lakes. In Nigeria, the Niger Delta is a famous example of wetland vegetation.
Ecological Significance of Wetland Vegetation
Flood Control – Wetlands act as natural sponges, absorbing excess water and helping to reduce flood risks.
Water Purification – Wetland plants filter out pollutants from water, improving its quality.
Habitat for Wildlife – Wetlands provide homes for aquatic plants and animals, including fish, frogs, and waterfowl.
Carbon Storage – Wetlands store large amounts of carbon, helping to mitigate climate change.
Example:
The Niger Delta wetland is vital for both biodiversity and the local economy, supporting fisheries and agriculture in the region.
Summary
Vegetation types are crucial for the health of the planet. Each type of vegetation, whether it’s forest, grassland, desert, or wetland, serves specific functions that support life. These functions include:
Biodiversity Support – Providing homes for countless species.
Carbon Sequestration – Helping to absorb carbon and reduce climate change.
Soil Protection – Preventing erosion and maintaining soil fertility.
Water Regulation – Ensuring clean water supplies and flood control.
By understanding these vegetation types and their importance, we can better appreciate how they contribute to the stability of our ecosystems.
Evaluation
- How do forests help in climate regulation?
- Why are grasslands important for grazing animals?
- How do desert plants survive in extreme conditions?
- What role do wetlands play in water purification?
- Give an example of a vegetation type found in Nigeria and explain its importance.
Fantastic job today! You now understand how the different vegetation types around the world contribute to the health of the environment. Keep up the great work and stay curious! I look forward to seeing you in our next exciting lesson!
