Back to: Computer Studies JSS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we shall be talking about the meaning of information transmission. Please enjoy the class!
Information Transmission – Meaning of Information Transmission
Information is the currency of the digital age. It’s the fuel that drives our innovations, shapes our decisions, and connects us across the globe. But how does this valuable resource travel from point A to point B? That’s where information transmission comes in.
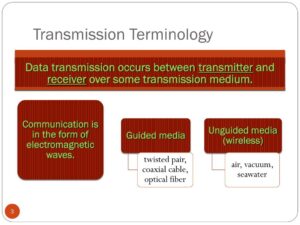
Information transmission is the process of sending and receiving information from one device or location to another. It involves three key components:
Sender: The origin of the information.
Channel: The medium through which the information travels (e.g., wires, airwaves, fiber optics).
Receiver: The destination of the information.
Information transmission is the foundation of all communication and data sharing. Without it, we wouldn’t have the internet, email, social media, or any of the other technologies that have revolutionized our lives. It’s crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments to exchange ideas, collaborate on projects, and stay informed.
Types of Information Transmission:
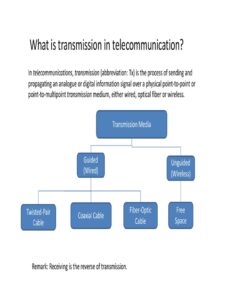
There are two main types of information transmission:
Analog: Information is represented by continuous waves that vary in amplitude or frequency. This is the traditional method used for radio and television broadcasts.
Digital: Information is converted into a series of binary digits (0s and 1s). This is the most common method used in modern computers and communication networks.
Key Concepts:
Data Rate: The speed at which information is transmitted, measured in bits per second (bps).
Bandwidth: The maximum amount of data that can be transmitted through a channel in a given time, measured in Hertz (Hz).
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR): The ratio of the strength of the desired information signal to the strength of unwanted noise.
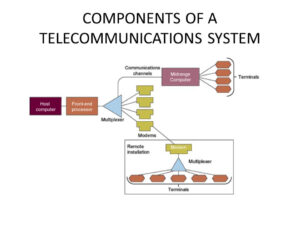
Transmission media: The physical means used to transport information, such as wires, cables, and radio waves.
Error detection and correction: Techniques used to identify and fix errors that occur during transmission.
Real-world examples includes;:
- Sending a message on WhatsApp
- Downloading a file from the internet
- Streaming a movie online
- Making a video call
As technology advances, information transmission is becoming faster, more reliable, and more accessible. We can expect to see even greater speeds, wider bandwidths, and more sophisticated error correction techniques in the future. These advancements will continue to fuel the growth of the digital world and connect us in ways we can only imagine.
In conclusion, Information transmission is a complex and fascinating topic that lies at the heart of our digital world. By understanding its principles and exploring its applications, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the technologies that connect us and shape our lives.
We have come to the end of today’s class. I hope you enjoyed the class!
In the next class, we shall be discussing Methods of Information Transmission.
In case you require further assistance or have any questions, feel free to ask in the comment section below, and trust us to respond as soon as possible. Cheers!
Question Time:
- What are the three key components involved in information transmission?
- What are the differences between analog and digital information transmission?
- How is data rate different from bandwidth?
- How does signal-to-noise ratio affect information transmission?
- What are some common methods for error detection and correction in information transmission?
