Back to: Computer Studies JSS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we shall be talking about the modes of information transmission. Please enjoy the class!
Modes of Information Transmission – Synchronous and asynchronous
Information is the lifeblood of the digital age, constantly flowing through networks and devices, connecting us and shaping our experiences. Understanding how this information travels efficiently and reliably is crucial for anyone involved in the computer science field. Today, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of information transmission, exploring two key modes: synchronous and asynchronous.
Imagine sending a message across the globe. It’s like sending a package on a journey, except the package is comprised of bits and bytes instead of physical objects. These bits, the fundamental building blocks of digital information, travel through various channels like cables, satellites, and even the airwaves. But how do they reach their destination accurately and without getting lost in the vast digital landscape? This is where the modes of information transmission come into play.
Synchronous Transmission:

Think of a synchronized dance performance. Everyone moves together in perfect unison, following the lead of a conductor. Synchronous transmission works in a similar way. Data is sent in continuous streams, like a flowing river, accompanied by timing signals generated by a central clock. This clock ensures the sender and receiver are perfectly coordinated, preventing data loss or errors.
Key characteristics of synchronous transmission:
Faster transmission: The constant pace minimizes delays and allows for efficient bulk data transfer.
Error-free: The timing signals ensure data integrity and prevent synchronization issues.
Complex setup: Requires dedicated hardware and software to maintain the clock synchronization.
Limited flexibility: Less suitable for situations with varying data transmission speeds.
Examples of synchronous transmission:
- Video conferencing
- Online gaming
- Telephony
- ATM transactions
Asynchronous Transmission:
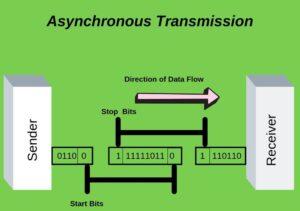
Imagine a group of friends texting each other. Each person sends messages at their own pace, without needing to wait for others. Asynchronous transmission operates in a similar fashion. Data is sent in individual units, like cars on a highway, each carrying its own control information. This allows for flexible and efficient communication, even when the sender and receiver are not in sync.
Key characteristics of asynchronous transmission:
Simple setup: Requires less complex hardware and software.
Flexible: Adapts to varying data transmission speeds and network conditions.
Error-prone: Susceptible to errors if control information is corrupted.
Slower transmission: Data transfer can be slower compared to synchronous transmission.
Examples of asynchronous transmission:
- Text messaging
- File transfers
- Social media posts
Choosing the Right Mode:
The choice between synchronous and asynchronous transmission depends on the specific needs of the application. For situations requiring high speed and accuracy, synchronous transmission is the preferred option. But for real-time communication and flexible data exchange, asynchronous transmission dominates the digital landscape.
Understanding these modes of information transmission is a valuable skill for any computer science student. It empowers you to design efficient and reliable communication systems, ensuring the smooth flow of information in our ever-connected world.
We have come to the end of today’s class. I hope you enjoyed the class!
In case you require further assistance or have any questions, feel free to ask in the comment section below, and trust us to respond as soon as possible. Cheers!
Question Time:
- Explain the difference between synchronous and asynchronous transmission in simple terms.
- What are the factors to consider when choosing between synchronous and asynchronous transmission for a specific application?
- How do timing signals play a role in synchronous transmission?
- What are the pros and cons of using start and stop bits in asynchronous transmission?
