Back to: Physical and Health Education JSS 2
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we shall be talking about the Types of postural defects. Please enjoy the class!
Types of Postural Defects
First things first, what’s good posture? Imagine a superhero standing tall, shoulders back, chin held high – that’s the posture we’re aiming for. It aligns your body, distributes weight evenly, and keeps your muscles working in harmony. But sometimes, life throws us curveballs (literally!), leading to:
- Kyphosis
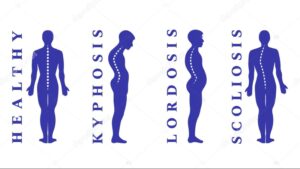
Picture a rounded upper back with hunched shoulders – that’s kyphosis. It can be mild, like a slouch from hours spent over textbooks, or more severe, like Scheuermann’s kyphosis.
The effects: Rounding your back compresses your lungs, making breathing less efficient. It can also pinch nerves, leading to neck pain, headaches, and even numbness.
Overcoming kyphosis:
Strengthen your back muscles: Superman back raises, rows, and yoga’s warrior poses are your allies.
Stretch your chest: Doorway chest stretches and foam roller massages will loosen those tight pecs.
Mind your posture: Set reminders, use ergonomic furniture, and consciously pull your shoulders back throughout the day.
- Lordosis
Imagine an exaggerated inward curve in your lower back, like rocking on your tippy toes. Lordosis can be caused by weak abdominal muscles or tight hamstrings.
The effects: Swayback puts extra strain on your lower back, leading to pain, stiffness, and even slipped discs. It can also shorten your hamstrings, impacting your flexibility.
Overcoming lordosis:
- Strengthen your core: Plank variations, crunches, and bridges will build a strong abdominal wall.
- Stretch your hamstrings: Lunges, hamstring stretches, and foam rolling will loosen those tight leg muscles.
- Wear supportive shoes: Choose shoes with good arch support to avoid further stressing your lower back.
- The Flatline:
Think of a spine that’s lost its natural S-shaped curves, resembling a board instead of a spring. Flat back syndrome can be caused by weak back muscles or tight hip flexors.
The effects: Flat back reduces your range of motion in your spine, making it harder to bend and twist. It can also lead to lower back pain and difficulty maintaining proper posture.
Overcoming flat back:
Mobilize your spine: Cat-cow exercises and gentle spinal twists will help restore movement to your spine.
Strengthen your back muscles: Bridges, deadlifts, and back extensions will engage your core and back muscles.
Stretch your hip flexors: Lunges, frog pose, and pigeon pose will release the tension in your hips and improve your pelvic tilt.
Question Time:
Objective questions:
- Which of the following is NOT a common type of postural defect?
- a) Kyphosis
- b) Lordosis
- c) Scoliosis
- d) Flat back syndrome
- What is the main characteristic of kyphosis?
- a) An inward curve in the lower back
- b) A rounded upper back with hunched shoulders
- c) An S-shaped curve in the spine
- d) A forward tilt of the pelvis
- Which muscles are most important for strengthening to prevent lordosis?
- a) Hamstrings
- b) Glutes
- c) Abdominals
- d) Chest muscles
- What is a potential consequence of flat back syndrome?
- a) Difficulty breathing
- b) Reduced range of motion in the spine
- c) Numbness in the hands
- d) Increased risk of knee injuries
- What is the best way to improve your posture throughout the day?
- a) Wear supportive shoes
- b) Take regular breaks to move around
- c) Set reminders to correct your posture
- d) All of the above
Essay questions:
- Discuss the causes and effects of kyphosis. What are some exercises that can help to improve kyphosis?
- Compare and contrast lordosis and flat back syndrome. How can you tell the difference between the two?
- Explain the importance of good posture for overall health and well-being. Describe some strategies for maintaining good posture throughout the day.
- Discuss the role of exercise in preventing and correcting postural defects. What specific exercises are beneficial for improving different types of postural defects?
- Research and discuss a specific postural defect that is not covered in class (e.g., scoliosis, rounded shoulders). Explain the causes, effects, and potential treatment options for this condition.
