Back to: BIOLOGY SS2
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s Biology class, We will continue learning about Adaptation in Nature. We hope you enjoy the class!

Adaptation of Animals in Marine Habitat
Barnacles have i. protection mantle for attachment to rock shore and water retention ii. Cilia for feeding. iii. A shell that prevents desiccation (drying up)
- Fishes possess
i. reduced or no kidney to retain urea in their body to cope with high salinity e.g. cartilaginous fishes like shark, dogfish e. t. c.
ii. Salt secreting glands in their gills or eyes for maintaining osmoregulation (salt balance) e.g. bony fishes like tilapia, herring e. t. c.
iii. Tube feet which enable them to hold on to rocky shores and hard shell to prevent desiccation e.g. starfish, whales.
2. Whales have
i. flippers for stability in water
ii. An organ in front of the nostril for detecting pressure changes in water.
iii. A thick layer of dermal fat insulation or food reservoir.
3. Shrimps possess powerful claws for holding food or prey.
4. Periwinkles possess lungs for breathing and foot for attachment.
5. Crabs burrow fast into the mud to protect them against predators, strong waves or hide.
Adaptation of Plants to Marine Habitat

Plants such as seaweeds, algae, and diatoms are naturally found in marine habitat with the following adaptive features;
- Seaweeds have
i. holdfast for attachment.
ii. mucilaginous cover to prevent desiccation.
iii. Divided leaves or floating devices for buoyancy.
2. Algae (e.g sargassum) have
i. chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
ii. Small size or large surface area for floating in the water.
3. Planktons (e.g. diatoms) possess;
i. air space in their tissues
ii. Rhizoid for attachment to rocks
iii. Air bladder for buoyancy (floating).
Adaptation in Estuarine
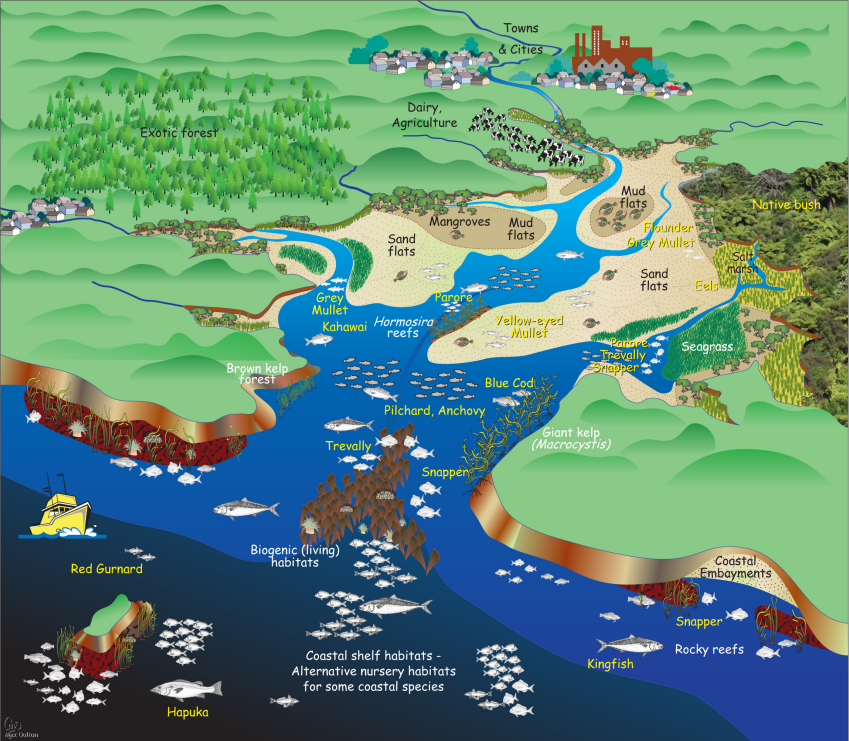
Plants found in estuaries include planktons, algae, red and white mangrove. They have the following adaptive features;
- Planktons (diatoms) have;
i. air spaces in their tissues
ii. rhizoid for the attachment to rock shores
iii. air bladder for buoyancy
2. Algae have
i. chlorophyll for photosynthesis
ii. small size or large surface area for floating in the water.
3. Red mangrove has;
i. stilt roots with rootlets that have air-spaces for air conduction to the root tissues and support to prevent washing away of the plant by the tide
ii. Seeds which germinate while they are still on the parent plant, thus preventing the carrying away of the seedlings by the water current.
4. White mangrove has pneumatophores (breathing roots) for gaseous exchange.
Animal Adaptation
Animals including mosquitoes, crustaceans, molluscs, worms, fishes e.t.c. found in estuaries survive possessing the following features;
- Mosquito larvae and pupae possess breathing trumpets for gaseous exchange
- Crustaceans and water snails burrow into the mud against predators, strong waves or tides.
- Worms have strong protective and impermeable covering against high salinity.
- Mudskippers have fins for crawling on land and swimming in water.
- Fishes have fins for movement and swimming bladder for buoyancy.
Evaluation:
- What is a freshwater habitat?
- Mention five animals dwelling in an estuary.
Plant Adaptation in Fresh Water
- Water lily has
i. air bladder
ii. expanded tips and lightweight which keep it afloat.
2. Spirogyra has a mucilaginous cover for protection
3. Water lettuce has hairs in leaves to trap air and keep it afloat
4. Waterweed (elodea) has a long and flexible petiole for swinging with water currents.
Animal Adaptation
- Protozoa have contractile vacuole for osmoregulation in water.
- Duck has webbed feet for locomotion and serrated beak for sieving food in water into its mouth.
- Hydra has slippery surface, hooks and suckers for attachment to water particles.
- Pondskatters has long legs for skating on the water surface.
- Fishes have swim bladders for buoyancy and gills for respiration.
THEORY
- List five characteristics of an estuary.
- State five adaptive features of animals in a freshwater habitat and their functions.
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
We have come to the end of this term. It’s been a remarkable journey and we are glad that you have made it this far. For making it this far, we commend you for being resilient, you have taken charge of your education and future.
The Journey still continues though, we are moving on to Second Term. we hope to meet you there.
