Back to: BIOLOGY SS2
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s Biology class, We will be learning about Transport System in Higher Plants. We hope you enjoy the class!
In simple unicellular plants, materials are exchanged by a simple diffusion process between the plants and their aquatic environment. Hence there is no need for an elaborate transport system. However, in the higher plant such as ferns and the flowering plants. There is a need for an elaborate transport system for transporting water and mineral salts from the soil to the various parts of the plants and also transport manufacture food from the leaves to other parts where it is either used up or stored up. The transport system of a plant is made up of vascular bundles consisting of the xylem and the phloem tissues.
The xylem is responsible for conducting water with dissolved substances from the soil to other parts of the plant. The phloem tissue is responsible for the transportation of manufactured food from the leaves to other parts of the plant (translocation). In the roots and stems of dicotyledonous plants, a layer called cambium exists between the xylem and the phloem tissues. The vascular bundles, therefore, are found in the roots, stems and leaves of flowering plants.
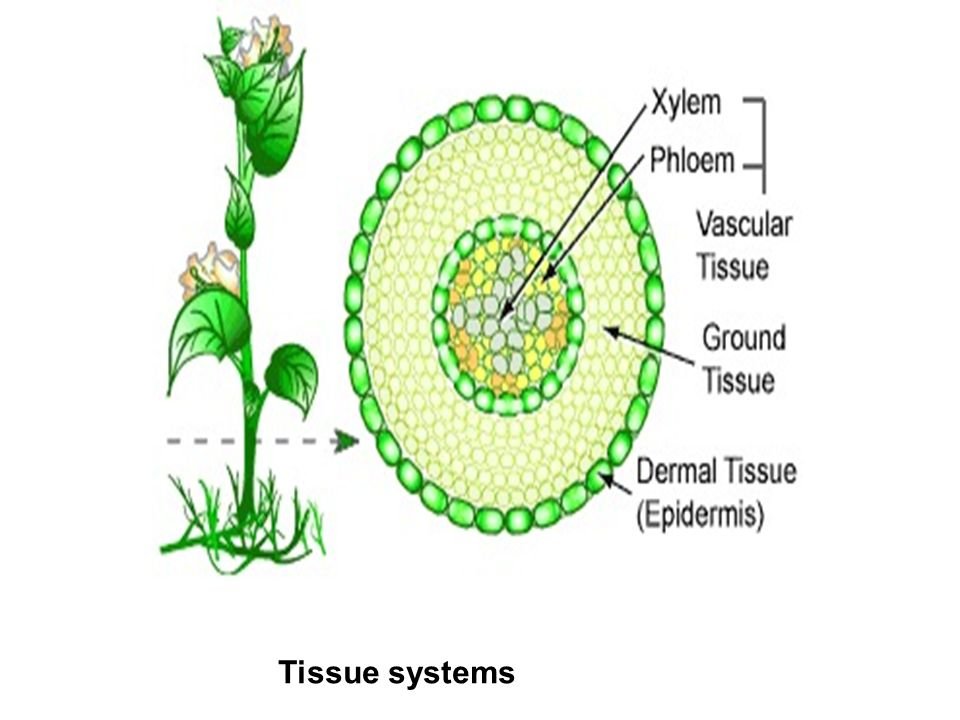
PROCESSES WHICH AID TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS
The four processes supporting transportation in plants are:
- Translocation: The process by which manufactured food substances are transported through phloem tissue from the site of production to plant tissues where they are used or stored. It is usually from leaves to other plant parts.
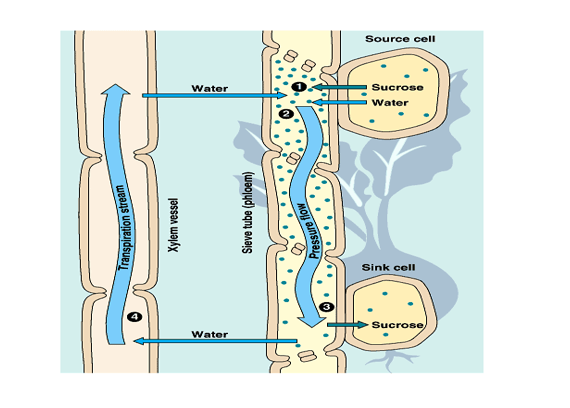

Transpiration: The removal of excess water from plants into the atmosphere in the form of water vapour. The loss of water can be through the stomata (in leaves) lenticels (in the stem) or cuticle of the leaf surface. The rate of transpiration is measured using the instrument potometer.
CONDITION AFFECTING THE RATE OF TRANSPIRATION
- The Size of the Stomatal Pores: Flaccidity of the guard cells causes them to close preventing transpiration but when turgidity occurs, the cells open for transpiration to take place.
- Humidity: The higher the humidity, the slower the rate of transpiration.
- Temperature: Increase in temperature leads to an increase in transpiration.
- Light: High light intensity causes a high photosynthetic rate which in turn leads to an increase in temperature thereby causing a high rate of transpiration.
- Wind: The higher the speed of the wind, the higher the rate of transpiration.
- Soil Water: A higher level of soil water leads to a higher rate of absorption which results in a higher rate of transpiration.
IMPORTANCE OF TRANSPIRATION TO PLANT
- It helps plants to absorb water and mineral salts from the soil.
- It facilitates the movement of soil water.
- Cooling the plant after water evaporation has taken place.
- Absorption of water and mineral salt by roots of plant water from the soil enters the plant through the root hairs by osmosis. This leads to increased turgor pressure of the vacuole of root cells. The water absorbed then gets into the xylem vessel
- Water transport in the xylem tissue: This is due to the following
- root pressure and suction pressure,
- Capillary action due to alteration between the water molecules and the walls of the xylem vessel,
- transpiration pulls.
GENERAL EVALUATION
- List the three main blood vessels in the human body
- State five differences between arteries and vein
- Draw and write a short note on the human heart
- Write a short note on transportation in plants
- List four processes that aid transportation in plants.
Reading Assignment
College Biology, Chapter 7, Page 159 – 169
WEEKEND ASSIGNMENT
SECTION A
- The rate of transpiration is measured using the instrument called A. photometer B potometer C. Secchi disc D. hygrometer.
- The process by which manufactured food substances are transported through phloem tissues from site of production to plant tissues where they are used is A. transpiration B. translocation C. active transport D. passive transport
- The following except one have closed circulatory system A. Snail B. earthworm C. man D. lion
- The semilunar valve is present in A. arteries veins C. capillaries D. Bladder
- The human heartbeat is ….. beats per minute A. 60 66 C. 72 D. 80
SECTION B
- With a well-labelled diagram, describe the human heart.
- Explain (a) root pressure (b) suction pressure
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will be learning about the Respiratory System. We are very much eager to meet you there.
