Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, brilliant learner! Imagine a tiny seed growing into a tall maize plant or a houseplant bending toward sunlight. What makes plants grow in specific directions? The answer is auxins—one of the most important plant hormones.
Today, we will learn about how auxins are made (biosynthesis) and how they move (transport) through the plant to control growth.
Biosynthesis and transport of auxins
What Are Auxins?
Auxins are plant hormones that regulate growth, cell elongation, and responses to light and gravity. They play a major role in:
✅ Stem elongation – Making plants grow taller.
✅ Root development – Helping roots grow deeper into the soil.
✅ Phototropism – Bending toward light.
✅ Gravitropism – Guiding root growth downward.
The most common and naturally occurring auxin in plants is Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA).
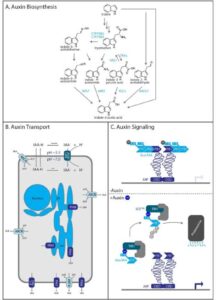
Biosynthesis of Auxins: How Are They Made?
Auxins are mainly produced in the shoot tips (apical meristem), young leaves, and developing seeds. Their production involves several steps:
Tryptophan Pathway:
Auxins are made from tryptophan, an amino acid found in plant cells.
Tryptophan is converted into Indole-3-pyruvic acid (IPA) by enzymes.
IPA is further modified into Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)—the active form of auxin.
Tryptophan-Independent Pathway:
Some plants can also make IAA without using tryptophan, but this pathway is less understood.
✅ Key Fact: Most auxins are produced in the growing tip of shoots and then transported downward to other parts of the plant.
Transport of Auxins: How Do They Move?
Unlike other hormones that move freely in plant tissues, auxins have a directional transport system. This means they move in a controlled, one-way manner called polar transport.
1. Polar Transport (Top to Bottom Movement)
Auxins move from the shoot tip to the root in a controlled way.
This movement happens through special transport proteins in plant cells.
Transport occurs in the phloem (vascular tissue) and through individual cells.
2. Carrier Proteins Control Auxin Movement
There are two main types of auxin transport proteins:
PIN proteins – Control auxin flow out of cells.
AUX1 proteins – Help auxin enter cells.
These proteins ensure auxins move downward, helping plants grow in the right direction.
How Do Auxins Control Growth?
Phototropism (Growing Toward Light)
When light shines on one side of a plant, auxins move to the shaded side, causing those cells to grow longer.
This makes the plant bend toward the light!
Gravitropism (Roots Growing Downward)
In roots, auxins slow down cell growth on the lower side, making roots bend downward into the soil.
In shoots, auxins encourage upward growth, helping the plant reach sunlight.
Apical Dominance (Why Side Branches Stay Small)
The shoot tip produces auxins that suppress the growth of side branches.
If the tip is cut off, side branches start growing because auxin levels decrease.
Why Is Auxin Transport Important?
✅ Helps plants bend toward light for better photosynthesis.
✅ Controls root and shoot development for strong growth.
✅ Maintains apical dominance, ensuring tall, healthy plants.
✅ Assists in fruit and seed development.
Summary
Auxins (especially IAA) control plant growth and responses to the environment.
They are mainly produced in the shoot tips, young leaves, and seeds.
Auxins are made from tryptophan through a series of chemical reactions.
They move downward in a controlled, polar transport system using PIN and AUX1 proteins.
Auxins help plants grow toward light (phototropism) and downward into soil (gravitropism).
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- Where are auxins mainly produced in plants?
- What is the role of PIN proteins in auxin transport?
- How do auxins help a plant bend toward light?
Fantastic job, superstar! You now understand how auxins are made and transported to control plant growth. Keep up the great learning, and see you in the next lesson!
