Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, my brilliant student! How are you doing today? Have you ever wondered how plants drink water from the soil? Unlike humans who use cups, plants have a built-in system that allows them to absorb water efficiently. This system is their roots, and today, we’ll explore how their structure helps them take up water to survive and grow.
Structure and Function of Plant Roots in Water Uptake
Roots are one of the most important parts of a plant because they anchor the plant in the soil and help absorb water and nutrients. The way roots are structured makes them perfect for this job. Let’s break it down!
1. Structure of Plant Roots
Plant roots have different parts, each with a special role in water uptake:
Root hairs: These are tiny, hair-like structures found on young roots. They increase the surface area, making it easier for the plant to absorb more water.
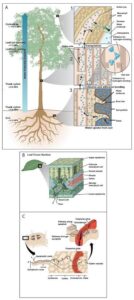
Epidermis: The outer layer of root cells. Root hairs grow from this layer and help in water absorption.
Cortex: The layer beneath the epidermis. It stores food and helps transport water to the inner parts of the root.
Endodermis: A single layer of tightly packed cells that control the movement of water into the plant’s vascular system.
Xylem: The transport tissue that carries water from the roots to the rest of the plant.
2. How Roots Absorb Water
Water enters the plant roots through a process called osmosis. Here’s how it happens:
Soil water has a higher water potential than the root cells, so water moves into the root hairs.
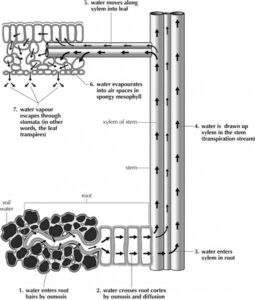
Water passes through the cortex by two pathways:
Apoplastic pathway (through spaces between cells).
Symplastic pathway (through the cytoplasm of cells).
The endodermis acts as a checkpoint. It has a waterproof strip called the Casparian strip, which forces water to pass through the cell membrane, ensuring only useful minerals enter the plant.
Water moves into the xylem, the plant’s water transport system, and is pulled upwards through transpiration pull, root pressure, and capillary action.
3. Functions of Roots in Water Uptake
Absorbing Water: Roots take up water from the soil, which is essential for photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and cooling the plant.
Transporting Water: Once inside, water moves upward to the leaves through the xylem.
Storing Nutrients: The cortex in roots stores food and minerals for the plant.
Providing Support: Roots anchor the plant firmly in the soil, preventing it from falling over.
Summary
Roots are specially structured to absorb and transport water efficiently. Root hairs increase absorption, the epidermis and cortex help in movement, and the xylem carries water to the leaves. Water moves into roots by osmosis and travels through different pathways before reaching the xylem. Without roots, plants wouldn’t survive!
Evaluation
- What is the main function of root hairs?
- How does water enter the root from the soil?
- What is the role of the xylem in water transport?
- Why is the endodermis important in water uptake?
You’re doing a fantastic job! The more you learn about plants, the more you’ll appreciate their amazing survival strategies. Keep going, and soon, you’ll understand plants better than ever. See you in the next lesson—Afrilearn is always here to make learning fun and easy for you!
