Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, brilliant learner! Have you ever wondered how a tiny maize seedling grows into a tall plant with strong roots, green leaves, and a healthy cob? What controls this entire process? The answer lies in hormonal regulation of growth!
Plants don’t have brains, but they still know when to grow, when to stop, and how to respond to their environment—all thanks to plant hormones. Today, we’ll learn how these hormones work together to control growth and development in plants.
Hormonal regulation of growth
How Do Hormones Regulate Plant Growth?
Plant growth is controlled by a balance of different hormones. These hormones work together like a team—some encourage growth, while others slow it down.

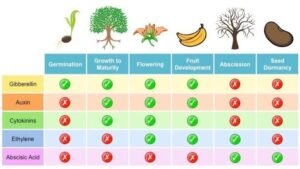
There are five key plant hormones involved in growth regulation:
Auxins – Promote stem and root growth.
Gibberellins – Stimulate stem elongation and seed germination.
Cytokinins – Promote cell division and leaf growth.
Abscisic Acid (ABA) – Slows down growth during stress.
Ethylene – Controls fruit ripening and shedding of leaves.
Each of these hormones has a special role, but they also interact with each other to ensure balanced growth.
Hormonal Interactions in Growth Regulation
1. Auxins and Growth Direction
Auxins help plants grow toward light (phototropism) and downward into the soil (gravitropism).
When light comes from one side, auxins move to the shaded side, causing cells to grow faster on that side and bending the plant toward the light.
In roots, auxins slow down cell growth on the lower side, making roots bend downward into the soil.
Example: If you place a potted plant near a window, it bends toward the light because auxins direct its growth.
2. Gibberellins and Stem Elongation
Gibberellins help plants grow taller by making cells expand. They also break seed dormancy, allowing seeds to germinate and grow into new plants.
Example: Farmers spray gibberellins on sugarcane to make the stems longer and increase yield.
3. Cytokinins and Cell Division
Cytokinins promote cell division, helping plants grow new tissues. They also work with auxins to maintain a balance between root and shoot growth.
Example: In tissue culture (artificial plant growing), cytokinins are used to produce many plants quickly.
4. Abscisic Acid (ABA) and Growth Inhibition
ABA is a stress hormone that slows down growth during tough conditions like drought. It causes stomata to close, reducing water loss and preventing seeds from sprouting too early.
Example: During harmattan, trees shed leaves because ABA stops unnecessary growth to conserve water.
5. Ethylene and Fruit Ripening
Ethylene speeds up fruit ripening and leaf shedding. When a fruit is ripe, ethylene softens it and changes its colour.
Example: A ripe banana releases ethylene, making nearby unripe bananas ripen faster.
Balance Between Growth-Promoting and Growth-Inhibiting Hormones
Plants need a balance between growth-promoting hormones (auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins) and growth-inhibiting hormones (ABA, ethylene).
For example:
In young plants → Auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins promote growth.
During stress (e.g., drought) → ABA slows down growth to conserve energy.
In ageing plants → Ethylene promotes fruit ripening and leaf fall.
This balance ensures healthy plant development.
Why Is Hormonal Regulation Important?
Ensures proper plant growth – Hormones control height, root depth, and leaf formation.
Helps plants respond to the environment – Light, gravity, and stress affect hormone levels.
Supports agriculture – Farmers use plant hormones to improve crop yield and fruit ripening.
Summary
Auxins control plant growth direction.
Gibberellins promote stem elongation and seed germination.
Cytokinins stimulate cell division and delay ageing.
Abscisic Acid (ABA) slows growth during stress.
Ethylene controls fruit ripening and leaf shedding.
A balance between these hormones ensures proper plant growth and adaptation.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- Which hormone helps plants grow toward light?
- How do gibberellins help in agriculture?
- Why do leaves fall off trees during the dry season?
You’re doing fantastic, superstar! Now you understand how plants control their growth using hormones. Keep up the great work, and see you in the next lesson!
