Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, brilliant learner! Have you ever seen plants shrivel during dry weather and wondered how they survive long periods without rain? Just like humans sweat to cool down, plants have special survival tricks to save water and resist drought. One key player in this process is abscisic acid (ABA), a powerful plant hormone that helps plants survive when water is scarce.
Today, we’ll learn how ABA functions in drought resistance and why it is crucial for plant survival.
Function of abscisic acid (ABA) in drought resistance
What Is Abscisic Acid (ABA)?
Abscisic acid (ABA) is often called the “stress hormone” of plants because it helps them respond to tough conditions like drought, cold, and heat. When a plant lacks water, ABA triggers emergency survival responses to conserve moisture and prevent dehydration.
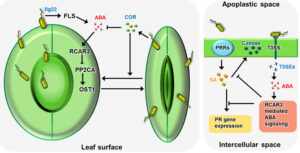
ABA plays a key role in:
✅ Closing stomata to reduce water loss.
✅ Slowing down growth to save energy.
✅ Triggering seed dormancy until conditions improve.
Now, let’s break these down.
1. How ABA Helps Plants Conserve Water
Plants lose water through tiny openings on their leaves called stomata. These stomata help in gas exchange, but during drought, they must close to prevent excess water loss.
How Does ABA Control Stomata?
When a plant experiences drought stress, ABA is produced in the roots.
The hormone travels to the leaves and signals the guard cells to close the stomata.
This prevents further evaporation and helps the plant retain water.
✅ Example: During dry seasons in Nigeria, crops like maize and cassava produce more ABA to survive without rain.
2. How ABA Slows Down Growth During Drought
When water is scarce, growing new leaves and stems wastes energy. ABA slows down plant growth so that the plant can survive longer without water.
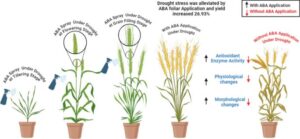
How Does ABA Reduce Growth?
It inhibits cell division in young shoots and leaves.
It reduces nutrient movement to growing parts of the plant.
It ensures the plant focuses on survival rather than growth.
✅ Example: If you notice grass turning brown during harmattan, it’s because ABA has slowed down its growth to save water.
3. How ABA Triggers Seed Dormancy
Seeds need moisture to germinate. If conditions are too dry, seeds won’t sprout, or they’ll die before they develop. ABA prevents seeds from germinating until there is enough water.
How Does ABA Control Germination?
It keeps seeds in a dormant state until conditions improve.
Once the environment is wet enough, ABA levels drop, and the seed starts growing.
✅ Example: Many Nigerian crops like beans and millet rely on ABA to delay germination until the rainy season.
Why Is ABA Important for Drought Resistance?
✔ Closes stomata to reduce water loss.
✔ Slows down plant growth to conserve energy.
✔ Keeps seeds dormant until conditions improve.
✔ Helps plants survive extreme weather like harmattan and dry spells.
Summary
ABA is a stress hormone that helps plants survive drought.
It closes stomata to prevent water loss.
It reduces plant growth to save energy.
It prevents seeds from germinating in dry conditions.
ABA is crucial for crops in dry regions like northern Nigeria.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- How does ABA help plants save water during drought?
- Why do some seeds stay dormant even when planted?
- What happens to plant growth when ABA levels increase?
Fantastic job, superstar! Now you understand how plants use ABA to survive harsh weather. Keep learning, and see you in the next lesson!
