Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, dear learner! I hope you’re having a great day! Have you ever wondered how a small maize seed grows into a tall, fruit-bearing plant? Or how a mango tree continues to grow year after year, producing new leaves and fruits? It all comes down to metabolism—the set of chemical processes that keep plants alive, growing, and developing. Today, we will look at why metabolism is so important for plant growth and development.
Importance of metabolism in growth and development
Metabolism is the backbone of a plant’s survival. Without it, plants wouldn’t be able to make their own food, break down nutrients for energy, or even repair damaged cells. Every stage of a plant’s life, from germination to maturity, depends on different metabolic processes.
Here are some key reasons why metabolism is crucial for plant growth and development:
Energy Production for Growth
Just like how we eat food to gain strength, plants rely on respiration to break down glucose and produce energy. This energy fuels cell division, which is necessary for a plant to grow from a seedling into a mature plant. Without metabolism, plants wouldn’t have the energy to increase in size or develop new structures.
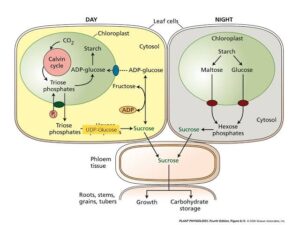
Food Production through Photosynthesis
Plants are unique because they make their own food through photosynthesis. This process, which takes place in the leaves, converts sunlight into chemical energy stored in glucose. This food is later used for growth, reproduction, and repair. Without metabolism, photosynthesis wouldn’t happen, and plants would starve.
Nutrient Transport and Uptake
Have you ever noticed how water and nutrients move from the roots to the leaves? This is made possible by metabolic processes. Active transport helps roots absorb minerals from the soil, while the xylem and phloem ensure that water, minerals, and food reach all parts of the plant. This movement supports growth and the development of new leaves, stems, and flowers.
Formation of New Cells and Tissues
As a plant grows, it continuously produces new cells. These cells come from cell division and differentiation, processes that require energy from metabolism. Whether it’s the formation of strong woody stems in trees or soft leaves in vegetables, metabolism plays a vital role in shaping the plant’s structure.
Response to Environmental Changes
Imagine a maize plant experiencing a dry season. How does it survive? Metabolism helps plants adapt to their environment by regulating water use, adjusting growth rates, and even producing protective chemicals. For instance, some plants slow down metabolism during droughts to conserve energy and survive harsh conditions.
Reproduction and Fruit Production
Without metabolism, plants wouldn’t be able to flower or produce fruits. Processes like flowering, pollination, and seed formation all require energy, which comes from metabolic activities. When you enjoy a juicy mango or a fresh orange, you’re benefiting from the plant’s efficient metabolism!
In summary, metabolism is the driving force behind plant growth and development. It provides energy for growth, enables food production, supports nutrient transport, aids in cell formation, helps plants adapt to their environment, and ensures successful reproduction. Without metabolism, plants wouldn’t survive, and life as we know it would be impossible!
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- How does metabolism help plants produce energy for growth?
- Why is photosynthesis an essential metabolic process in plants?
- How does metabolism help plants survive environmental challenges like drought?
Well done, superstar! You’re doing an amazing job learning about how plants grow and develop. Keep going, and remember—every big tree you see started as a tiny seed with the help of metabolism. See you in the next lesson!
