Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, amazing learner! Have you ever planted a seed and watched it grow into a big, leafy plant? Think about how a small maize seed can turn into a tall stalk with many cobs. How does this happen? How does a single seed produce roots, stems, and leaves? The answer lies in two important biological processes: growth and differentiation.
Today, we’ll learn how plants grow, how their cells change into different types, and why these processes are important for plant survival.
Concept of growth and differentiation
What is Growth?
Growth is the permanent increase in the size and mass of an organism. In plants, growth happens through cell division and enlargement.
For growth to take place, plants need:
Nutrients (from the soil)
Water (for metabolic processes)
Sunlight (for energy)
Hormones (to regulate growth)
Types of Growth
Primary Growth – Increases the length of the plant. It occurs in the apical meristems (tips of roots and shoots).
Secondary Growth – Increases the thickness of the plant. It occurs in the vascular cambium (which produces wood in trees).
Example from Everyday Life:
If you measure a young cassava plant today and check again in two weeks, it will be taller. That increase in height is growth!
Wat is Differentiation?
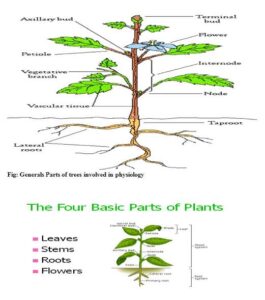
Differentiation is the process where plant cells become specialised for different functions. Not all cells in a plant remain the same—some become roots, leaves, or flowers.
This process allows plants to:
Develop different structures (roots, stems, leaves).
Perform specialised functions (photosynthesis, water transport).
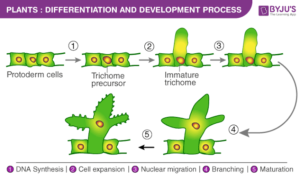
Stages of Differentiation
Cell Division – New cells are produced through mitosis in the meristems.
Cell Enlargement – Cells grow in size by taking in water.
Cell Maturation – Cells change into specific types (e.g., root cells absorb water, leaf cells perform photosynthesis).
Example from Everyday Life:
In a yam plant, some cells become roots (to absorb water), some become stems (to support the plant), and others become leaves (to make food). This is differentiation in action!
Why Are Growth and Differentiation Important?
Plants cannot survive without these processes!
Growth helps plants reach sunlight, absorb water, and spread their roots.
Differentiation ensures that plants have the right structures to carry out life processes.
Summary
Growth is the increase in size and occurs through cell division and enlargement.
Differentiation is when cells become specialised for different functions.
Growth can be primary (length) or secondary (thickness).
Without differentiation, plants would not develop proper roots, leaves, or stems.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- What is the difference between primary and secondary growth?
- Why is differentiation important for plants?
- Which plant structure is responsible for cell division and growth?
Fantastic job, superstar! Now you understand how plants grow and develop into different structures. Keep learning, and see you in the next lesson!
