Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, my brilliant student! How are you doing today? Have you ever noticed how the leaves of a plant sometimes look fresh and firm in the morning but begin to droop under the hot afternoon sun? This is because plants are constantly losing water through a process called transpiration. Today, we’ll learn what transpiration is, how it works, and why it’s important for plant survival.
Definition and Significance of Transpiration
What is Transpiration?
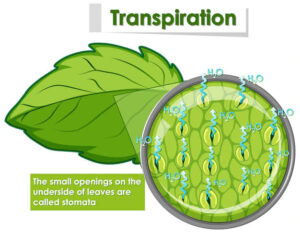
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the aerial parts of a plant, mainly through the stomata in the leaves. This process occurs when water evaporates from the plant’s surface into the atmosphere.
Think of it like sweating in humans. When you sweat on a hot day, your body loses water, but this helps to cool you down. Similarly, plants lose water through transpiration, which plays an important role in their growth and survival.

How Does Transpiration Happen?
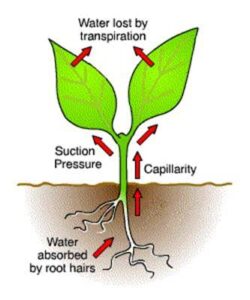
Water is absorbed by the roots from the soil.
It moves up through the xylem to reach the leaves.
Tiny pores on the leaves called stomata open to allow gas exchange.
Some of the water escapes as vapour into the air.
The rate of transpiration depends on factors like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and light intensity.
Why is Transpiration Important? (Significance of Transpiration)
Even though plants lose water through transpiration, this process is essential for their survival. Let’s look at why:
Cooling the Plant
Just like sweating cools our bodies, transpiration cools down the plant. When water evaporates from the leaves, it reduces the plant’s temperature, preventing heat damage.
Helps in Water and Mineral Transport
Transpiration creates a pulling force that helps move water and minerals from the roots to the leaves through the xylem. This is called the transpiration pull, which ensures that every part of the plant gets the nutrients it needs.
Maintains Turgidity (Firmness) in Cells
When plants lose water, the cells inside them shrink, making the plant wilt. A proper balance of transpiration keeps the cells filled with water, ensuring the plant stays upright and strong.
Facilitates Photosynthesis
For photosynthesis to happen, plants need to take in carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air. When stomata open for transpiration, they also allow CO₂ to enter, making food production possible.
Regulates Water Balance
Transpiration prevents plants from absorbing too much water, which could damage their cells. It helps maintain a steady water balance inside the plant.
Is Too Much Transpiration Harmful?
Yes! While transpiration is beneficial, excessive water loss can cause plants to dry out and wilt. This is why some plants, like cacti, have adaptations to reduce transpiration, such as small leaves and thick waxy coatings.
Summary
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from plant leaves through stomata. It plays a crucial role in cooling the plant, transporting water and minerals, maintaining cell firmness, facilitating photosynthesis, and regulating water balance. However, too much transpiration can lead to water loss and wilting.
Evaluation
- What is transpiration, and how does it occur in plants?
- Name three important functions of transpiration.
- How does transpiration help in water and mineral transport?
- What happens when a plant loses too much water through transpiration?
Fantastic work! You’ve just unlocked the secret behind how plants manage their water. Keep up the great learning—Afrilearn is always here to make your learning journey fun and easy. See you in the next lesson!
