Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, dear learner! I hope you’re having a fantastic day! Have you ever wondered why we breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide? Or why plants need oxygen at night even though they produce it during the day? The answer lies in a very important process—the electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation.
These processes produce the majority of ATP—the energy currency of cells. They happen inside the mitochondria and ensure that plants, animals, and all living things have enough energy to grow, move, and survive. Today, we’ll break it down in a way that’s easy to understand!
Electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation
What Is the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)?
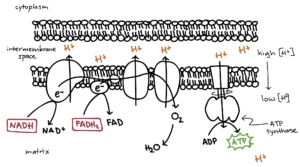
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) is the final stage of cellular respiration. It occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria, where high-energy electrons (from NADH and FADH₂) are used to generate ATP.
Steps of the Electron Transport Chain
Electron Donation
The NADH and FADH₂ molecules (produced in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle) donate high-energy electrons to protein complexes in the mitochondria.
Electron Transfer & Proton Pumping
As electrons move through the ETC, their energy is used to pump protons (H⁺) into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient (high concentration of H⁺ outside the inner membrane).
Oxygen as the Final Electron Acceptor
At the end of the chain, oxygen (O₂) accepts the electrons and combines with protons to form water (H₂O).
Without oxygen, the entire chain stops working!
What Is Oxidative Phosphorylation?
This is the final step where the proton gradient created by the ETC is used to make ATP.
Steps of Oxidative Phosphorylation
Protons Flow Back into the Mitochondria
Protons (H⁺) want to move from high concentration (outside) to low concentration (inside) through an enzyme called ATP synthase.
ATP Production
As protons pass through ATP synthase, their movement powers the production of ATP from ADP.
This process generates about 34 ATP molecules—the most ATP produced in cellular respiration!
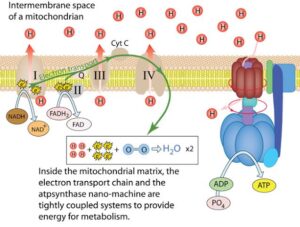
Why Is This Process Important?
Produces Most of the Cell’s ATP – Without the ETC, cells wouldn’t have enough energy to function.
Uses Oxygen Efficiently – The ETC ensures that oxygen is used effectively to release energy.
Prevents Energy Waste – Instead of releasing all energy at once (which would be harmful), the ETC releases it gradually.
Summary
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) transfers electrons through a series of proteins, using their energy to pump protons across the membrane.
Oxidative Phosphorylation uses this proton gradient to drive ATP production.
Oxygen is essential because it acts as the final electron acceptor, allowing the cycle to continue.
This process produces the most ATP (about 34 molecules), making it the powerhouse of energy generation.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- Where does the Electron Transport Chain (ETC) occur?
- What is the role of oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation?
- Why is ATP synthase important?
Well done, superstar! You’ve just unlocked one of the most important energy-making processes in all living things. Keep up the great work, and see you in the next lesson!
