Back to: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING SS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about the final accounts of a sole trader. Enjoy the class!
Final Accounts of a Sole Trader

CONTENTS
- Contents of the Final Accounts of a Sole Trader
- The Trading Account – Contents and Preparation
- The Profit and Loss Account – Contents and Preparation
The final accounts of a sole trader consist of the following
- The Trading Account
- The Profit and Loss Account
- The Balance Sheet
The trading account:
The Trading Account is prepared to ascertain the Gross Profit or the Gross Loss of the business for the trading period.
- The Gross Profit is the difference between the sales revenue and the cost of goods sold
- The Cost of goods sold is derived by adding the Opening Stock to the Net Purchases and deducting the Closing Stock from the ensuing total.
- Net Purchases is derived by deducting Returns Outwards (i.e. Purchases Returns) from the Purchases figure.
- Sales revenue (or Net Sales) is derived by deducting Returns Inwards (i.e. Sales Returns) from the Sales figure.
- It is usual to add the cost of transporting the goods to the trader’s shop i.e. Carriage Inwards to the Purchases figure when deriving the Cost of Goods Sold
- The Cost of goods sold is also referred to as the Cost of Sales
The Trading Account must have a heading which includes the period of time covered by the statement (or account). It is also usual to include the name under which the business trades. There are two ways in which a Trading Account can be prepared – horizontal and vertical.
- The horizontal format or T – format is similar to a traditional ledger account. Using this method, the Sales revenue is shown on the credit side and the Cost of goods sold on the debit side. The difference (or balance) between the two sides equals the Gross Profit or Gross Loss for the period.
The Gross Profit is carried down to the Profit and Loss Account
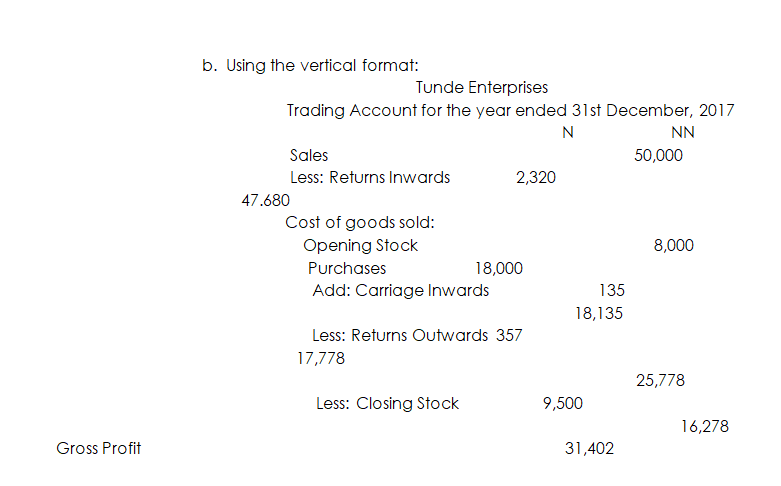
- A Trading Account can also be prepared using the vertical format. This is the format used by most businesses. A Trading Account prepared using this method contains the same information as in a horizontal format, but looks like an arithmetic calculation.
Illustration:
The following balances were extracted from the books of Tunde Enterprises for the year ended 31st December 2017.
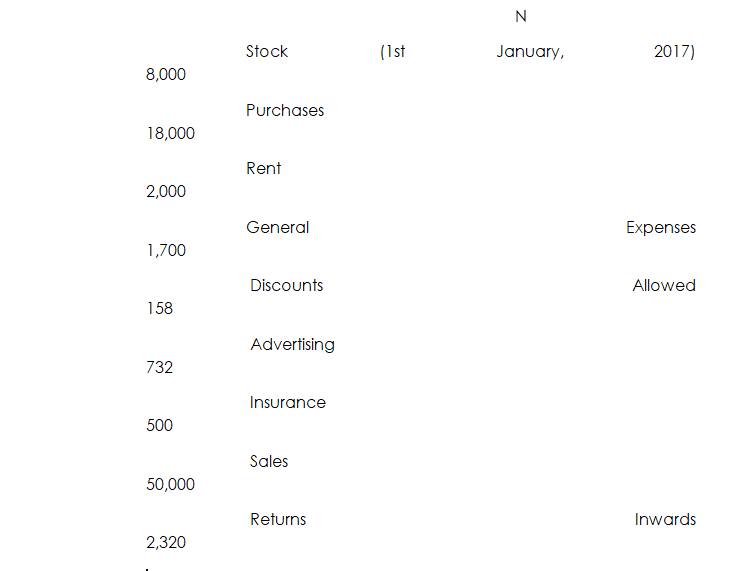

The value of Stock at close on 31st December 2017 was N9,500
You are required to prepare the Trading Account for the year ended 31st December 2017.
- Using the horizontal or T – format:

Evaluation
- List three features of the Trading Account
- State three components of the final accounts of a sole trader.
The profit and loss account
The profit and loss account is concerned with profits and losses, gains and expenses. Its purpose is to calculate or ascertain the Net Profit or Net Loss for the period.
The formula for calculating net profit is: Net Profit = Gross Profit + other income – Expenses
The Profit and Loss Account must have a heading which includes the period of time covered by the statement. It is also usual to include the name under which the business trades.
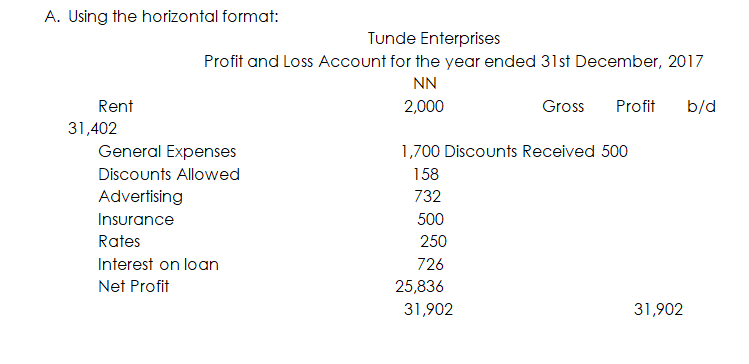
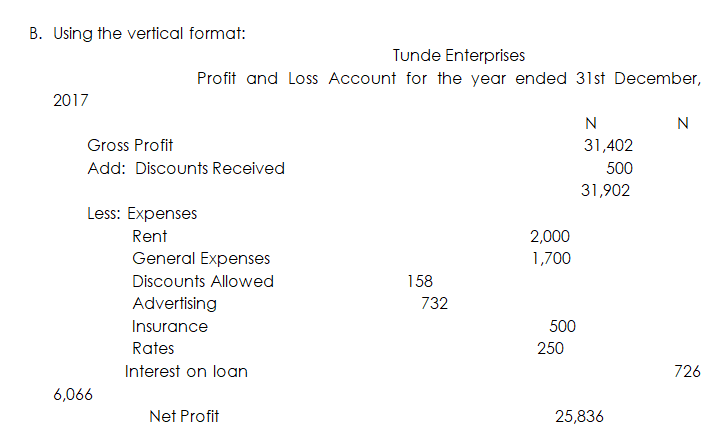
As with a Trading Account, a Profit And Loss Account can be prepared using either the horizontal or the vertical method. Using the horizontal format, the gross profit and any other income are shown on the credit side and the expenses are shown on the debit side. The difference (or balance) between the two sides equals the Net Profit or Net Loss for the year.
The Net Profit /Net Loss is transferred to the Capital Account.
Illustration:
Using the list of balances shown in the earlier illustration, prepare the Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st December 2017.
Evaluation
- List four features of the Profit and Loss Account
- List three similarities and two differences between the Trading Account and the Profit and Loss Account
Reading assignment
- Simplified and Amplified Financial Accounting Page 180 – 187
- Business Accounting 1 Page 49 – 57
General evaluation
- List five source documents that are used in preparing the Cash Book
- State five advantages of using the Imprest system to keep petty cash transactions
- List five benefits of keeping accounting records
- State ten uses of the General Journal
- List eight contents of the Trading Account of a sole trader.
Weekend assignment
- Carriage inwards as an expense of a business is treated in the ………..…(a) Trading Account (b) Profit and Loss Account (c)Balance Sheet (d) Appropriation Account.
Use the following information to answer question 2 to 5
. N
Purchases 168,000
Sales 183,400
Opening Stock 20,100
Closing Stock 48,900
Carriage Outwards 2,400
Carriage Inwards 5,000
Return Inwards 10,000
Expenses 15,000
Return Outwards 8,000
- The gross profit is………. (a) N47,200 (b) N42,200 (c) N37,200 (d) N19,800
- The net profit is…………(a) N42,200 (b) N37,200 (c) N19,800 (d) N47,200
- The cost of goods sold is ………..(a) N185,100 (b) N139,200 (c) N136,200 (d) N131,200
- The cost of goods available for sale was……….. (a) N188,100 (b) N173,000 (c) N193,100 (d) N190,700
Theory
- List three uses of each of the following financial records /information.
- Cash Book
- Profit and Loss Account
- List ten items of expenses that are charged (or debited) to the Profit and Loss Account of a sole trader.
In our next class, we will be talking more about Final Accounts of a Sole Trader. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

This content is rich and helpful. Both Teachers and learners will derive benefit from it
it’s simple and self-explanatory.
thanks for making a side copy of school syllabus.