Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, my brilliant student! How are you today? I hope you’re feeling great because today’s lesson is another exciting one! Have you ever noticed that when you soak dry beans in water, they swell up? Or when you sprinkle salt on vegetables, they start releasing water? These are everyday examples of osmosis and diffusion, two important processes that help plants survive and grow.
Osmosis and Diffusion in Plants
Plants, just like humans, need a way to transport substances in and out of their cells. This is where osmosis and diffusion come in. These two processes help plants absorb water, distribute nutrients, and get rid of waste. Let’s break them down.
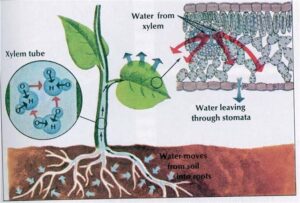
Diffusion (Movement of Molecules from High to Low Concentration)
Diffusion is the movement of molecules (like gases or dissolved substances) from an area where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated, without needing energy.
Real-life Example: Have you ever walked into a kitchen and immediately smelled delicious jollof rice, even though the pot is far from you? That’s because the aroma spreads through diffusion—the smell moves from where it is strong (the pot) to where it is weak (the rest of the room).
In Plants:
Diffusion helps plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air through tiny openings on their leaves (stomata) for photosynthesis.
It also allows oxygen, a waste product of photosynthesis, to diffuse out into the air.
Nutrients like minerals also move into plant roots through diffusion when their concentration is higher in the soil than inside the plant cells.
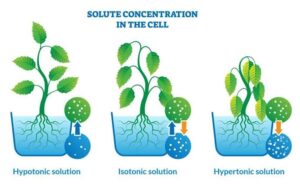
Osmosis (Movement of Water through a Semi-Permeable Membrane)
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration, across a semi-permeable membrane (a barrier that allows only some substances to pass).
Real-life Example: Have you ever placed a slice of cucumber in salty water and noticed that it shrinks and becomes soft? That’s because water moves out of the cucumber cells into the salty water by osmosis.
In Plants:
Roots absorb water from the soil through osmosis. The soil usually has more water than the root cells, so water moves into the plant.
If a plant is placed in salty or dry soil, water can move out of its cells, making it wilt. That’s why too much fertiliser or drought can harm plants!
Osmosis also helps maintain the shape and firmness of plant cells, keeping
them strong and upright.
Summary
Diffusion and osmosis are essential for plant survival. Diffusion allows gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen to move in and out of plants, while osmosis helps plants absorb water and stay firm. Without these processes, plants wouldn’t be able to grow, photosynthesise, or even stand upright!
Evaluation
- What is diffusion, and how does it help plants?
- How do plants absorb water from the soil?
- Give one real-life example of osmosis.
- Why do plants wilt when there is too much salt in the soil?
Great job today! You are getting smarter with every lesson, and I am so proud of you. Keep going, and remember—learning about plants is learning about life! See you in the next lesson—Afrilearn is always here to make learning fun and easy for you!
