Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, dear learner! I hope you’re doing well today. Have you ever wondered how a tiny seed grows into a mighty tree, producing food, flowers, and fruits without eating like we do? It may look like plants are just standing still, but inside, they are busy with many processes that keep them alive and thriving. This is where metabolism comes in. Today, we will look at how plants manage their energy and nutrients to survive and grow.
Overview of metabolic processes in plants
Metabolism in plants refers to all the chemical processes that take place inside their cells to support life. Just like we need food to stay active, plants need energy to grow, repair themselves, and produce oxygen. These processes can be divided into two main types:
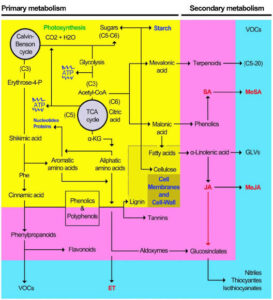
Anabolism – This involves building up. Plants use simple substances like carbon dioxide and water to make complex molecules like glucose, which stores energy. The most common anabolic process is photosynthesis, where plants use sunlight to produce food.
Catabolism – This is the breaking down of complex substances to release energy. A key example is respiration, where glucose is broken down to provide energy for the plant’s activities, just like how we eat food to gain strength.
Some of the important metabolic processes in plants include:
Photosynthesis – This is how plants make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. The result? Glucose for energy and oxygen for us to breathe! It happens mainly in the leaves, inside tiny structures called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for trapping sunlight.
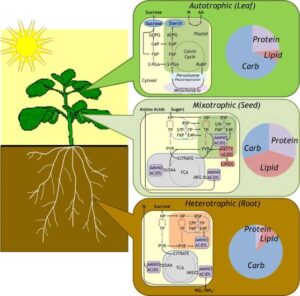
Respiration – After making food, plants need to release the energy stored in it. This happens through respiration, which occurs in the mitochondria, often called the “powerhouse” of the cell. Just like how our body burns food for energy, plants break down glucose to produce energy, water, and carbon dioxide.
Protein and enzyme synthesis – Plants also produce proteins that help in growth and defence. For instance, they absorb nitrogen from the soil to form amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. These proteins help plants grow strong and fight off diseases.
Transport of nutrients and water – Even though this is not a chemical reaction, it is essential for metabolism. Plants transport water and minerals from the roots to the leaves through the xylem, while food moves from the leaves to other parts through the phloem. This process ensures that all parts of the plant get the nutrients they need.
In summary, plants are not passive beings; they carry out several processes to stay alive and grow. Photosynthesis helps them make food, respiration releases energy, and other metabolic activities ensure they have enough nutrients and proteins to function properly. Without these processes, plants wouldn’t be able to survive, and neither would we!
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- What are the two main types of metabolism in plants?
- Why is photosynthesis considered an anabolic process?
- What is the role of respiration in plants?
You are doing great! Keep up the enthusiasm, and remember—plants may not move, but they are constantly working hard behind the scenes. Stay curious, and I’ll see you in the next lesson!
