Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, superstar learner! Have you ever noticed how a plant bends toward light or how some plants grow taller than others? This isn’t magic—it’s the work of a powerful plant hormone called auxin!
Today, we’ll learn how auxins control cell elongation and help plants respond to light through phototropism. Get ready for an exciting journey into how plants “sense” their environment and grow!
Role of auxins in cell elongation and phototropism
What Are Auxins?
Auxins are plant hormones that regulate growth and development. They are mainly produced in the shoot tips (apical meristems), young leaves, and developing seeds. The most common auxin in plants is Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA).
Auxins play a role in:
✅ Cell elongation – Making cells grow longer.
✅ Phototropism – Helping plants bend toward light.
✅ Root and shoot development – Controlling plant height and depth.
Role of Auxins in Cell Elongation
What is cell elongation?
Cell elongation is the process where plant cells grow longer, making the plant taller or its roots deeper. Auxins trigger this process by loosening the cell wall, allowing the cell to expand.
How Does Auxin Promote Cell Elongation?
Auxins activate proton pumps → These pumps release hydrogen ions (H⁺) into the cell wall.
Cell walls become acidic → This weakens the bonds holding the cell wall together.
Expansins (special proteins) are activated → They break the rigid connections in the cell wall, making it more flexible.
Water enters the cell, increasing turgor pressure → The cell stretches and becomes longer.
✅ Result: The plant grows taller and its roots grow deeper.
Role of Auxins in Phototropism
What is phototropism?
Phototropism is the way plants grow toward light. This is important because it helps plants capture more sunlight for photosynthesis.
How Do Auxins Control Phototropism?
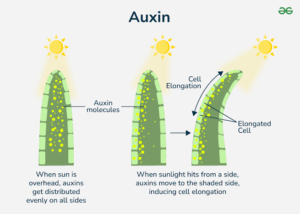
Light hits one side of the plant → This causes auxins to move to the shaded side.
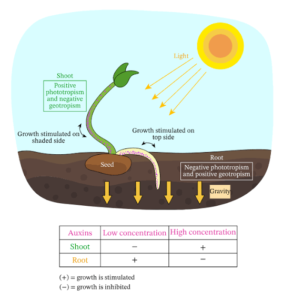
Cells on the shaded side grow longer → Auxins stimulate cell elongation on the darker side.
The plant bends toward the light → The uneven growth causes the shoot to curve toward the light source.
✅ Example: If you place a young maize plant near a window, you’ll see it bend toward the light after a few hours!
Why Are These Functions Important?
✅ Cell elongation helps plants grow taller, allowing them to compete for sunlight.
✅ Phototropism ensures that leaves get maximum exposure to sunlight for photosynthesis.
✅ Controlled growth allows plants to develop strong roots and shoots for survival.
Summary
Auxins (especially IAA) help plant cells grow longer through cell elongation.
They activate proton pumps and expansins, making the cell walls flexible.
Phototropism happens when auxins move to the shaded side of a plant, causing it to bend toward light.
These processes help plants grow taller, stronger, and more efficient in capturing sunlight.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- How do auxins help cells grow longer?
- What is phototropism, and why is it important?
- Why do auxins move to the shaded side of a plant during phototropism?
Great job, superstar! You now understand how auxins control growth and help plants respond to light. Keep up the fantastic learning, and see you in the next lesson!