Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, dear learner! I hope you’re doing great today! Have you ever wondered where the energy in your body comes from? Whether you’re walking, reading, or even sleeping, your body constantly needs energy. The same goes for plants—they need energy to grow, transport nutrients, and survive. But where does this energy come from?
Meet the mitochondria, the “powerhouse of the cell”! This tiny but mighty organelle is responsible for producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of all living cells. Today, we’ll break down the role of mitochondria in energy production so you can understand why they are one of the most important parts of a plant cell.
Role of mitochondria in energy production
What Is the Mitochondrion?
The mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is a small, double-membraned organelle found in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells. It has its own DNA and ribosomes, meaning it can produce some of its own proteins.
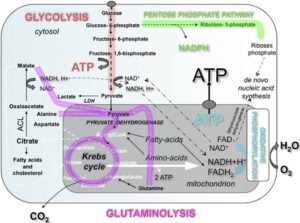
The mitochondria’s main function is to generate ATP through a process called cellular respiration. This process breaks down glucose in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP, which powers all cell activities.
Structure of the Mitochondrion and Its Functions
The mitochondrion has a unique structure that helps it efficiently produce energy. Let’s look at its parts:
Outer Membrane – This protects the mitochondrion and controls what enters and leaves.
Inner Membrane – This is highly folded into structures called cristae, which increase the surface area for ATP production.
Matrix – This is the fluid-filled space inside the inner membrane where the Krebs cycle takes place.
Intermembrane Space – The area between the inner and outer membranes where protons (H⁺) accumulate to drive ATP production.
How Mitochondria Produce Energy
Energy production in the mitochondria happens in three major stages of cellular respiration:
1. Glycolysis (Outside the Mitochondria, in the Cytoplasm)
Glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing 2 ATP molecules.
Pyruvate then enters the mitochondria for further breakdown.
2. Krebs Cycle (In the Mitochondrial Matrix)
Pyruvate is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂) and generating NADH and FADH₂ (high-energy molecules).
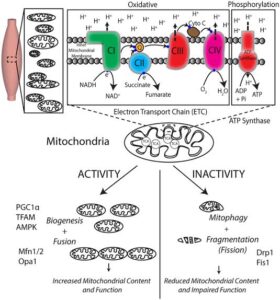
2 more ATP molecules are produced.
3. Electron Transport Chain & Oxidative Phosphorylation (In the Inner Membrane)
NADH and FADH₂ donate electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC).
These electrons help pump protons (H⁺) into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient.
Protons flow back through an enzyme called ATP synthase, which produces 34 ATP molecules.
Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, combining with hydrogen to form water (H₂O).
Total ATP Produced: About 36–38 ATP per glucose molecule!
Why Are Mitochondria Important?
They produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
They regulate metabolism, ensuring cells get enough energy.
They help maintain proper oxygen use in plant and animal cells.
They support growth and development by providing energy for cell division and repair.
Summary
The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, producing ATP through cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration happens in three stages: Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain.
The inner membrane of the mitochondrion is folded into cristae, increasing the surface area for ATP production.
Oxygen is essential for the final step of ATP production, making mitochondria vital for energy generation.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- Where does the Krebs cycle take place in the mitochondria?
- What is the function of the electron transport chain?
- Why are cristae important in the mitochondria?
Excellent work, superstar! You’ve just unlocked the secrets of how mitochondria produce energy for all living cells.Keep learning, and see you in the next lesson!
