Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, brilliant learner! Have you ever wondered how plants know when to flower or when to grow taller? Unlike humans, they don’t have eyes to see light, yet they respond to it perfectly! This is possible because of phytochromes, special light-sensitive proteins that help plants detect and respond to light.
Today, we’ll learn about the role of phytochromes in light perception, why they are important, and how they help plants survive and grow in the best conditions.
Role of phytochromes in light perception
What Are Phytochromes?
Phytochromes are light-sensitive proteins found in plants. They help plants detect red and far-red light, allowing them to regulate important processes like seed germination, flowering, and shade avoidance.
Think of phytochromes as the plant’s light switches—they help plants know when to start or stop growing based on the type of light they receive.
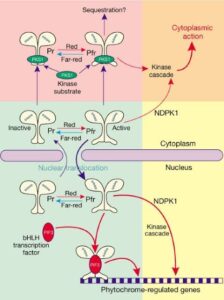
How Do Phytochromes Work?
Phytochromes exist in two interconvertible forms:
Pr (Phytochrome red) – Absorbs red light (660 nm).
Pfr (Phytochrome far-red) – Absorbs far-red light (730 nm).
When a plant is exposed to red light (daylight), Pr changes into Pfr, which is the active form that triggers growth and development.
At night or under shade (far-red light), Pfr converts back to Pr, slowing down growth.
This switching mechanism helps plants sense day and night, as well as detect shade from other plants.
Functions of Phytochromes in Plants
1. Seed Germination
Many seeds require red light to germinate. When phytochromes detect enough red light, they signal the seed to sprout.
✅ Example: Lettuce and tomato seeds will not germinate well in the dark because they need Pfr to trigger germination.
2. Control of Flowering
Plants use phytochromes to determine the length of day and night, helping them know when to flower at the right season.
Short-day plants (e.g., yam, rice) flower when nights are long.
Long-day plants (e.g., spinach, lettuce) flower when nights are short.
This ensures plants flower at the best time for pollination and seed production.
3. Shade Avoidance
When plants grow in crowded areas, they receive more far-red light (Pr), which signals them to grow taller to reach sunlight.
✅ Example: If maize is planted too close together, the plants will stretch upwards to avoid shade from their neighbours.
4. Leaf Expansion and Chlorophyll Production
Plants use phytochromes to control leaf size and chlorophyll levels. If they detect too little light, they adjust leaf growth to capture more sunlight.
✅ Example: Shade plants like ferns grow wider leaves to maximise light absorption.
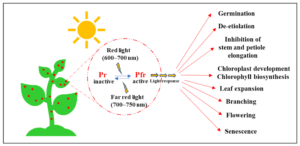
Why Are Phytochromes Important?
✔ Help seeds germinate at the right time.
✔ Ensure plants flower in the correct season.
✔ Prevent plants from being shaded by taller neighbours.
✔ Allow plants to adjust their growth to changing light conditions.
Summary
Phytochromes are light-sensitive proteins that help plants detect red and far-red light.
Pr (red-light absorbing) and Pfr (far-red light absorbing) switch between each other based on light conditions.
Phytochromes regulate seed germination, flowering, shade avoidance, and leaf development.
They help plants grow at the right time and in the best conditions.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- What are the two forms of phytochromes, and how do they function?
- How do phytochromes help plants avoid shade?
- Why do some seeds need red light to germinate?
Amazing job, superstar! Now you understand how plants “see” light and adjust their growth. Keep shining, and see you in the next lesson!
