Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, brilliant learner! Have you ever wondered why some plants taste bitter, smell strong, or have bright colours? Why does bitterleaf have a harsh taste, and why does eucalyptus have a powerful scent? These characteristics are not just for fun—plants produce special chemicals called secondary metabolites to protect themselves from predators, diseases, and environmental stress. Interestingly, humans also benefit from these compounds in medicine, food, and industry.
Today, we’ll break down the role of secondary metabolites in plant defence and their applications in human life.
Role of secondary metabolites in plant defense and human applications
How Do Secondary Metabolites Help Plants Defend Themselves?
Unlike primary metabolites (which help plants grow and survive), secondary metabolites are mainly for protection. They help plants in three major ways:
Defence Against Herbivores – Some secondary metabolites have bitter or toxic properties that make plants unappetising to animals and insects.
Defence Against Microorganisms – Certain compounds have antibacterial, antifungal, or antiviral effects that protect plants from diseases.
Environmental Adaptation – Some secondary metabolites help plants survive in harsh conditions like drought, excess sunlight, or poor soil.
Now, let’s look at the different types of secondary metabolites and how they work in plant defence.
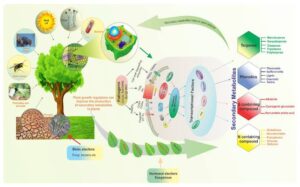
Types of Secondary Metabolites and Their Defence Roles
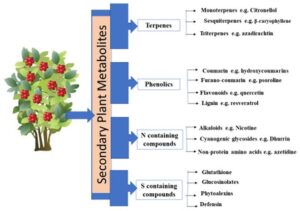
Alkaloids – These bitter compounds deter herbivores and protect plants from insects.
Example: Nicotine in tobacco repels insects.
Everyday Life: Bitterleaf soup gets its bitter taste from alkaloids, which protect the plant from being eaten.
Flavonoids – These colourful compounds protect against UV radiation and attract pollinators.
Example: Anthocyanins give hibiscus and grapes their red and purple colours.
Everyday Life: Zobo drink (made from hibiscus) is rich in flavonoids, which act as antioxidants.
Terpenoids – These fragrant compounds repel herbivores and attract pollinators.
Example: Limonene in citrus peels keeps insects away.
Everyday Life: Scent leaf (nchuanwu) releases a strong aroma due to terpenoids, helping repel insects.
Phenolics – These compounds fight infections and protect against stress.
Example: Tannins in unripe fruits make them taste dry and bitter, discouraging animals from eating them too early.
Everyday Life: Tea contains tannins, which give it a slightly bitter taste and help fight infections.
How Do Humans Benefit from Secondary Metabolites?
Many secondary metabolites have important uses in medicine, food, and industry. Let’s see how!
1. Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Many medicinal drugs come from plant secondary metabolites.
Alkaloids (like quinine) are used to treat malaria.
Terpenoids (like taxol) are used in cancer treatment.
Phenolics (like resveratrol) help prevent heart diseases.
Example: When you take herbal medicine for a cough, it may contain terpenoids that help soothe the throat.
2. Food and Nutrition
Some secondary metabolites act as antioxidants and improve food quality.
Flavonoids in fruits help prevent aging and diseases.
Terpenoids in spices (like ginger and turmeric) improve digestion.
Example: When you drink green tea, the flavonoids inside help boost your immune system and keep you healthy.
3. Cosmetics and Perfumes
Many terpenoids and phenolics are used in perfumes, lotions, and soaps.
Limonene from citrus fruits gives perfumes a fresh scent.
Eugenol from cloves is used in toothpaste and mouthwash.
Example: The strong scent of eucalyptus oil in balms helps clear blocked noses.
4. Pest Control and Agriculture
Some secondary metabolites help in natural pest control.
Pyrethrins (from chrysanthemum flowers) are used in insecticides.
Neem oil (from neem leaves) acts as a natural pesticide.
Example: Farmers use neem leaf extracts to protect crops from pests instead of chemical pesticides.
Summary
Secondary metabolites help plants defend themselves from herbivores, diseases, and harsh environments.
Alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolics all play different defence roles.
Humans benefit from secondary metabolites in medicine, food, cosmetics, and agriculture.
Many natural medicines, perfumes, and insect repellents are made from plant secondary metabolites.
Let’s Test Your Understanding:
- Name two secondary metabolites that help plants defend against herbivores.
- How do flavonoids benefit both plants and humans?
- Why are terpenoids important in perfumes and insect repellents?
You’re doing amazing, superstar! Now you understand how plants protect themselves and how we use their natural defences in everyday life. Keep up the great work, and see you in the next lesson!
