Back to: Botany 200 Level
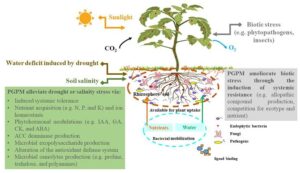
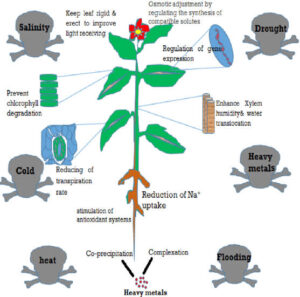
Hello, my brilliant student! How are you today? Have you ever seen a plant dry up during a long period without rain or struggle to grow in salty soil? These are signs of water stress, a condition where plants do not get enough water or receive water with too much salt. Today, we’ll learn about the two main types of water stress—drought stress and salinity stress—and how they affect plant growth.
Types of Water Stress (Drought, Salinity)
Water stress occurs when plants cannot absorb enough water due to either a lack of water (drought stress) or too much salt in the water (salinity stress).
1. Drought Stress – When Water is Scarce
Drought stress happens when a plant does not get enough water from the soil for an extended period. This can be caused by:
Lack of rainfall
High temperatures (causing excessive transpiration)
Poor soil water retention
Effects of Drought Stress on Plants:
Wilting – Leaves lose water and become limp.
Reduced photosynthesis – Without enough water, plants cannot produce food efficiently.
Leaf drop – Some plants shed their leaves to conserve water.
Slow growth – Water is essential for cell expansion, so plants grow slowly under drought conditions.
Death of the plant – If drought lasts too long, the plant may dry up completely.
Example: Imagine not drinking water for a whole day under the hot sun. You would feel weak and dehydrated. Plants feel the same way when they don’t get enough water!
2. Salinity Stress – When Water Contains Too Much Salt
Salinity stress occurs when plants absorb water that has a high concentration of salts. This is common in:
Coastal areas with salty groundwater.
Soils that have been over-irrigated with salty water.
Areas where fertilisers have built up too much salt in the soil.
Effects of Salinity Stress on Plants:
Difficulty absorbing water – Too much salt makes it harder for roots to take in water.
Leaf burning and yellowing – Salt damages leaf tissues, causing brown, dry edges.
Stunted growth – Plants struggle to grow because salt affects nutrient absorption.
Wilting, even with water – The plant may have water in the soil, but too much salt prevents it from using the water properly.
Example: Think about drinking seawater when you are thirsty—it doesn’t quench your thirst because of the high salt content. Similarly, plants cannot use salty water effectively.
How Do Plants Cope with Water Stress?
Plants have developed adaptations to survive in drought or salty conditions:
Deep roots – Some plants grow long roots to reach underground water.
Thick leaves – Plants like aloe vera store water in their thick leaves.
Salt glands – Some plants, like mangroves, have special glands that remove excess salt.
Leaf wax – A waxy coating on leaves reduces water loss.
Summary
Water stress affects plants when there is too little water (drought stress) or too much salt in the water (salinity stress). Drought stress causes wilting, slow growth, and leaf drop, while salinity stress prevents water absorption, damages leaves, and stunts growth. Some plants develop special adaptations to survive in these harsh conditions.
Evaluation
- What is drought stress, and what causes it?
- How does salinity stress affect plant growth?
- Why do plants wilt during drought?
- Name one adaptation that helps plants survive water stress.
Great job today! Now you understand how plants struggle and adapt to survive in dry or salty environments. Keep up the great learning—Afrilearn is here to make your journey fun and easy. See you in the next lesson!
