Back to: Botany 200 Level
Hello, my brilliant student! I hope you’re having a great day! Have you ever wondered why some plants grow so well with very little water, while others need frequent watering? This is because different plants have different abilities to use water efficiently. Today, we’ll be learning about the Concept of Water Use Efficiency (WUE)—a crucial factor that determines how well a plant can grow with the water it absorbs.
What is Water Use Efficiency (WUE)?
Water Use Efficiency (WUE) is a measure of how effectively a plant uses water to produce biomass or yield. Simply put, it answers the question: “How much growth or food does a plant produce for each drop of water it uses?”
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
WUE=Biomass or Yield ProducedWater UsedWUE = \frac{\text{Biomass or Yield Produced}}{\text{Water Used}}
For example, if two plants receive the same amount of water but Plant A produces more leaves, fruits, or grains than Plant B, then Plant A has a higher WUE.
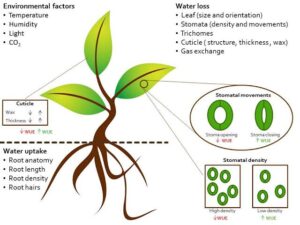
Why is Water Use Efficiency Important?
Maximises Crop Yield with Less Water – In regions with scarce water (e.g., Northern Nigeria), farmers can grow more food with efficient water use.
Helps Plants Survive Drought – Plants with high WUE can thrive in dry conditions, making them more resistant to climate change.
Reduces Water Waste – Efficient plants and farming methods ensure that water is not wasted through excessive evaporation or runoff.
Saves Farmers’ Costs – Less water usage means lower irrigation costs for farmers.
Types of Water Use Efficiency
There are different ways to measure WUE, depending on the focus.
Intrinsic WUE (Photosynthetic WUE):
This is the ratio of carbon dioxide (CO₂) absorbed to water lost through transpiration.
Plants that can absorb more CO₂ while losing less water have a higher intrinsic WUE.
Agronomic WUE:
This is the amount of crop yield (grains, fruits, or vegetables) produced per unit of water used.
Important for farmers because it determines how much food can be grown with available water.
Irrigation WUE:
Measures how much of the water applied through irrigation is actually used by plants instead of being lost to runoff or evaporation.
Important in agriculture to ensure efficient water management.
How Do Plants Improve Water Use Efficiency?
Plants have different ways of using water more efficiently.
Stomatal Control
Plants regulate the opening and closing of stomata (tiny pores on leaves) to reduce water loss while maximising CO₂ absorption.
Example: Cacti and succulents keep their stomata closed during the day to prevent excess water loss.
Leaf Modifications
Some plants have thick, waxy leaves or small, needle-like leaves to reduce water loss.
Example: The baobab tree stores water in its thick trunk and has small leaves to minimise evaporation.
Deep or Extensive Root Systems
Plants with deep roots can reach underground water, while those with wide root networks can absorb water from a large area.
Example: Millet and sorghum have deep roots, making them drought-resistant crops in Nigeria.
Efficient Photosynthesis Pathways
Some plants have special photosynthesis mechanisms that help them use water better:

C3 Plants (e.g., rice, wheat) – Normal photosynthesis but use more water.
C4 Plants (e.g., maize, sugarcane) – Use water more efficiently by reducing photorespiration.
CAM Plants (e.g., pineapple, cactus)– Absorb CO₂ at night to reduce daytime water loss.
How Farmers and Scientists Improve WUE
Drip Irrigation – Delivers water directly to the roots to prevent waste.
Mulching – Covering the soil with organic materials to reduce evaporation.
Plant Breeding – Developing crop varieties that use water more efficiently.
Soil Management – Adding organic matter to improve water retention.
Summary
Water Use Efficiency (WUE) measures how effectively plants use water to grow.
High WUE means a plant produces more biomass with less water.
Plants improve WUE through stomatal control, deep roots, waxy leaves, and special photosynthesis.
C4 and CAM plants have higher WUE compared to C3 plants.
Farmers can improve WUE through irrigation, mulching, and better crop selection.
Evaluation
- What is Water Use Efficiency (WUE)?
- How does stomatal control help plants save water?
- Which type of plant has higher WUE: maize or rice? Why?
- What are two ways farmers can improve WUE in agriculture?
- Why do C4 and CAM plants have better WUE than C3 plants?
Great job! You now understand why some plants thrive in dry areas while others need constant watering. Keep learning—Afrilearn is here to make learning simple and fun! See you in the next lesson!
