Back to: CHEMISTRY SS3
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about aromatic hydrocarbon. Enjoy the class!
Aromatic Hydrocarbon
Benzene is a typical aromatic compound with a molecular formula of C6H6. It has the structure of:
Preparation
- From coal tar: The destructive distillation of coal produced coal tar which contains benzene
- From petroleum: The dehydrogenated of alkane using vanadium(v)oxide (v2O5) as a catalyst at 500oC and 20 atmos give benzene
C6H14 V2O2 → C6H6 + 4H2
The process is known as catalytic reforming.
- From polymerization of ethyne:
3 ( H – C = C – H ) → C6H6
Evaluation
- Describe three (3) ways of preparing benzene.
- Draw the structure of benzene.
Physical properties
- It has a pleasant odour.
- It has a boiling point of 80oC.
- Benzene can dissolve in water.
- It burns with a sooty flame.
Chemical properties
Benzene can undergo both an additional reaction and substitutional reaction.
Additional reaction:
- Hydrogenation: Benzene reduces to cyclo-hexane if hydrogen gas is passed through finely divided nickel at 150oC.
- Halogenation: In the presence of ultra-violet light, benzene reacts with halogen to produce a cyclic compound.
- Substitution reaction.
- Benzene undergoes substitution reaction due to the presence of its single bonds.
- Halogenation e.g. Cl2, Br2, I2
Nitration:
This occurs in the mixture of HNO3 and H2SO4 together with benzene
Alkylation:
It involves reactions of benzene with halo-alkanes in the presence of AlCl3.
Uses
- It is used as a solvent to dissolve organically.
- It is used as a fuel in petrol.
- It is used in the manufacture of aromatic compound e.g. benzoic acid.
Evaluation
- State two (2) uses of benzene
- Identify two (2) chemical properties of benzene with examples.
Derivatives of benzene
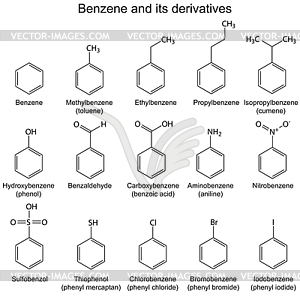
General evaluation
- Give another name to the following compounds (a) Phenol (b) Toluene
- State four (4) derivatives of benzene.
Reading assignment
New School Chemistry By .O.Y. Ababio, pg 492-494.
Weekend assignment
- Benzene can be prepared from the following except (a) Coal tar (b) petroleum (c) Alkanol (d) Ethyne
- Benzene can undergo additional reaction due to the presence of (a) double bonds (b) single bonds ( c) hydrogen ( d) carbon.
- Benzene undergoes the following reaction except. (a) substitution (b) addiction (c) Hydrogenation ( d) polymerization
- The technique used in separating a mixture of common salt and water is (a) evaporation (b) sublimation (c) decantation (d) chromatography.
Theory
- a. State two (2) uses of Benzene
- identify two (2) physical properties of benzene.
- a. How would you prepare benzene?
- State two (2) chemical properties of benzene.
In our next class, we will be talking about Alkanols. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

Interesting
hi