Back to: GEOGRAPHY SS3
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about karst (limestone) topography. Enjoy the class!
Karst (Limestone) Topography
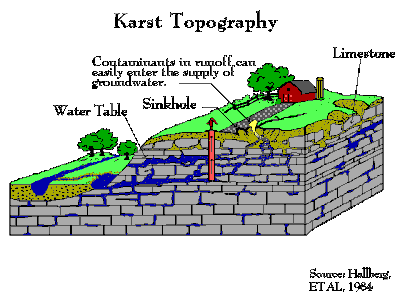
A limestone region refers to a large stretch of land occupied by limestone which possesses a unique type of topography. Limestone is a sedimentary rock of organic materials made up of calcium carbonate.
Characteristics of the limestone region
- Solubility: Limestone is dissolved in rainwater containing carbon dioxide to form a weak acid. Such rainwater acts on limestone and dissolves it.
- Presence of depressions: Limestone regions contain depressions of different sizes and depths.
- Absence of surface drainage: Due to easy permeability of water into the soil in a limestone region, most of the streams flow for a short distance and disappear underground.
- Absence of thick vegetation cover: The region is very dry hence, there is a complete absence of thick or luxuriant vegetation cover.
- Presence of dry surface valleys: Due to easy penetration of water in this region, all the valleys are dry. When water meets hard rocks underground, it may re-emerge below the limestone as spring or resurgence.
- Presence of joint and rugged topography: The blocks of rocks are joined together with fissures which allow water to pass through them and the surface is undulating.
Surface features of the limestone region
- Grike: It is formed as a result of progressive widening of cracks or joint by a solution to form a limestone pavement. Such enlarged pavements are called grikes.
- Clints: They are surface features of isolated and rectangular blocks which exist between joints or grikes.
- Swallow Holes or Sink Holes: These are small depressions carved out by solution where rainwater sinks into the limestone at a point of weakness.
- Doline: This is formed when several swallow holes join together to form a larger depression.
- Uvala: This results when several lines join to form a larger depression.
- Polges: These are formed partly by faulting, to form a larger depression.
Underground features of a limestone region
- Caves or Caverns: They are large underground spaces that are formed as a result of sinking and flowing of water into the limestone region through joints and bedding planes. They may contain stalactites and stalagmites. They may also contain rivers or ponds.
- Limestone Gorge: This has a vertical side formed when the roof of an underground cave collapses or when a river cuts across and runs down into a limestone region.
- Resurgence or Spring: This results from water sinking underground. When the water meets hard rocks underground, it re-emerges at the surface to form spring or resurgence.
- Stalactites: They are found in caves and they grow from up downward and may join stalagmite to form a pillar. Stalactites are sharp, slender and hang on the roof of caves. They are formed when water dripping down the cave carves out sharp and slender pinnacles. They are precipitates of calcium carbonate in the solution of the underground water.
- Stalagmites: These are also found in caves but they grow from down-upwards and may join stalactite to form a pillar. They are shorter, fatter and more rounded.
Stalagmites are formed when water drips down from stalactite to the floor; evaporation then occurs while calcium is deposited to form stalagmite.
- Pillars: Natural pillars are formed when stalactites growing from the roof join stalagmites growing from the floor of the caves.
Important limestone regions in Nigeria include Ewekoro, Sagamu (Ogun State), Okpella (Edo State), Nkalagu (Anambra State), Ashaka(Benue State) etc.
Importance of the limestone region
- Limestone region provides limestone which is an essential raw material for making cement.
- Limestone is also used in the smelting of tin and iron.
- Limestone area is a beautiful site of tourism.
- It is also a source of underground water.
- It provides grazing lands for animals.
Evaluation
- Mention four characteristics of a limestone region.
- Limestone is made up essentially of what mineral?
General evaluation
- What is an artesian well?
- Differentiate between an artesian basin and a well.
- State the importance of limestone region.
- Mention factors that can affect the weather and climate of an area.
- How does climate affect man’s activities?
Reading assignment
Essential Geography, Pages, 37-39.
Weekend assignment
- Stalagmite and stalactite are found in ………. (a) caves (a) huts (c) desert regions (d) plunge pool
- The main element in the limestone region is (a) oxygen (b) nitrogen (c) calcium carbonate (d) oxygen
- One of these areas in Nigeria is not a limestone region(a) Okpella, Edo State (b) Ewekoro, Ogun State (c)Kafanchan, Kaduna State (d) Shagamu, Ogun State
- A place where water issues out from the ground naturally is called a ……… (a) pond (b) spring (c) pool (d) well
- When a hole is sunk into the ground far below the water table and water seeps out of the rocks into the hole, it refers to a ……… (a) well (b) river (c) spring (d) fountain
Theory
- Write three differences between a stalactite and a stalagmite.
- What is the mode of formation of a pillar?
In our next class, we will be talking about Denudational Processes/Weathering. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
