Back to: Mathematics Primary 3
In math, money can be defined as the medium of exchange such as notes, coins, and demand deposits, used to pay for commodities and services. Money is anything that is a legal tender, generally accepted as a means of exchange, payment of goods and settlement of debt.
The value or price of item or service is paid for using money.
Motive For Holding Money
- Transactionary motive: we hold money in order to meet our daily demands. E.g. feeding, transportation, clothing, etc.
- Precautionary motive: we hold money because of unforeseen circumstances. E.g. health issues, death, etc.
- Speculative motive: we hold money to get more money. E.g. buying of shares, engaging in profitable business.
100kobo = N1
Note: when converting to naira, you divide by 100 and when converting to kobo, you multiply by 100.
Example:
Convert 500kobo to naira

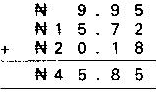
Addition of money
Example:
![]()
Subtraction of money.
Example:
![]()

Word Problem on Money
(a). Bola bought packet of pencil for ₦50.52, a book for ₦28.32 and an eraser for ₦5.00, how much did he spend?
Solution
Packet of pencil = ₦50.52
A Book = ₦28.32
An Eraser = ₦5.00
Total Amount = ₦83.84
(b). A man went to the market with ₦ 90.50. If he spent ₦25.76 on a book, how much balance did he collect?
Solution
Total amount taken to market = ₦90.50
Total amount spent = ₦25.76
Balance left = ₦64.74
Quiz
- Eden purchased a packet of candy for ₦76.52, a juice for ₦28.32 and a strawberry for ₦5.00, how much did she spend?
- A man went to the supermarket with ₦50. If he spent ₦85.76 on a toy, how much balance did he collect?
