Back to: COMMERCE SS2
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s Commerce class, We will be learning about Terms of Trade and Payment. We hope you enjoy the class!

CONTENT
- Documents exchanged between buyers and sellers – their features and use
- Common trade terms
- Terms of payment
- Common abbreviations
We continue learning about the document used in the Purchase and Sale of Goods from our last lesson…
NOTES
- PRO FORMA INVOICE: This is a document sent by a supplier to a prospective buyer informing him what he is likely to pay if he buys the goods concerned. The Pro forma invoice is similar to an invoice except that the words PRO FORMA is written across its face. It is sent mainly to inform the prospective buyer/customer about the prices of goods. It is not a document of indebtedness.
CIRCUMSTANCES IN WHICH A PRO FORMA INVOICE IS USED
- The seller uses it as a polite way of refusing the buyer credit when it is asked for. It is used when the wholesaler does not wish to sell on credit
- When goods are sent to an agent who will organize their sales
- It is used when goods are sent on inspection either for the customer to accept or return the goods to the seller within an agreed period
- It is used to reject an order that is too small
- It is used when repairs and servicing are carried out for which no charge is made
- It is sent when a quotation is asked for by the customer
- It serves as a reply to a letter of enquiry because it shows the prices of goods
- It can be used as a basis for the calculation of duty by the customs authority
- CREDIT NOTE: This is a document, usually printed in red, sent by the seller to inform the buyer that the sum specified in the credit note has been credited to his account thereby reducing the amount charged on the invoice.
A credit note is used to correct errors discovered in the invoice which overcharge the buyer.
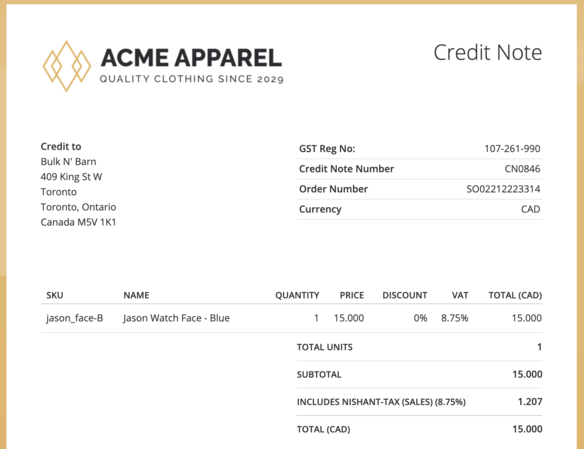
REASONS FOR ISSUING A CREDIT NOTE
A credit note is sent when:
- An overcharge has been made i.e. a credit note is issued to correct the overcharge
- When the buyer returns goods for some reasons e.g. not as ordered or if goods are damaged
- Packing cases or empties or returnable e.g. bottles, crates, cartons cylinders – already charged for are returned to the seller
- Gift vouchers are presented by the buyer
- Invoices are sent in error – a credit note is used in this case to cancel the wrong invoice
- DEBIT NOTE: This is a document sent by the seller to inform the buyer that the sum specified in the debit note has been debited to his account as a result of an error discovered in the invoice sent earlier which undercharged him.
The debit note informs the buyer that he owes more than the sum stated on the invoice sent earlier. The extra sum of money the buyer owes is stated in the debit note.
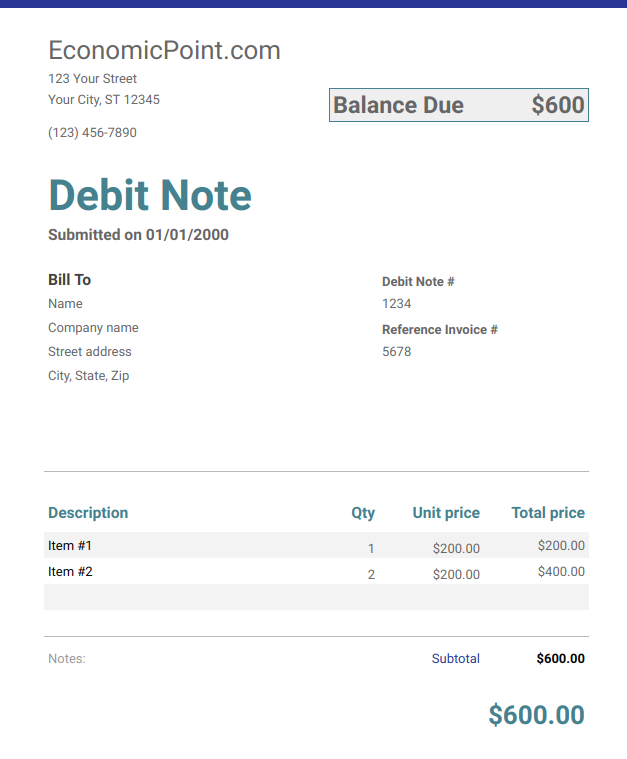
REASONS FOR ISSUING A DEBIT NOTE
A debit may be sent when:
- Goods are undercharged i.e. a debit note is issued to correct the undercharge
- Omissions are made on the invoice i.e. goods sent to the buyer are not charged on the invoice
- The buyer fails to return returnable packing cases or empties not charged for in the invoice
- If the invoice is inadequately priced
- When goods dispatched are more than the ones invoiced
The debit note, therefore, serves as an additional (or a supplementary) invoice since it is used to increase the amount charged on the invoice sent earlier.
- STATEMENT OF ACCOUNT/STATEMENT: This is a document sent out by a supplier (seller) to each customer at the end of each month or at some regular intervals showing:
- The opening balance i.e. balance brought forward – Bal. b/f
- The closing balance – balance outstanding at the end of the period – Bal c/f
- The dates and amount of the invoices rendered during the current period
- The payments received from the retailer during the period i.e. cash, cheques etc
- Particulars of any other credits i.e. the amounts of credit notes issued in favour of the retailer during the period
- The amounts of debit notes issued against the retailer during the period
PAYMENTS: The buyer can pay for the good he bought in cash or with other means of payment e.g. cheques, bank drafts, postal order, money order, credit transfer etc.
9. RECEIPT: This is a document issued by the seller to acknowledge payment made by the buyer
USES OF THE RECEIPT
- It shows evidence of payment
- It is used for auditing purposes
- It is a title of ownership (i.e. proof of ownership of the property)
- STATUS INQUIRY/REFERENCE LETTERS
When the buyer requests for credit especially in the first instance he usually supplies the names of businesses of firms with whom he has previous dealings as referees.
The seller can ascertain the buyer’s financial position, business experience and integrity by referring to the bankers of the buyer. This is known as carrying out a status inquiry.
A reference letter can also be written to firms provided as referees for the same purpose.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- State four instances in which a Pro-forma invoice is used.
- What is the difference between a statement and an invoice
- List and explain the first five document used in trade
TRADE TERMS
These are the various terms used in commerce (i.e. buying and selling of goods). The common trade terms are:
- DISCOUNT: Discount is the reduction in the price of goods given by a seller to a buyer to encourage bulk purchase and prompt payment. A discount decreases the amount someone pays when buying goods.
TYPES OF DISCOUNT
- Cash Discount: This is an allowance given to a customer to encourage payment for goods and services within a stipulated period of time. It is conditional in that the customer must pay promptly to enjoy the cash discount.
- Trade Discount: This is the reduction in the catalogue price of goods made by a seller in order to encourage customers to make bulk purchases or to provide for the retailer’s profit margin. It is usually based on a percentage of the total price of goods invoiced.
- Quantity Discount: This is offered by the supplier to the retailers as an inducement to buy large quantities of goods in a single order. The objective of the supplier on this case is to reduce his operational costs e.g. transportation cost.
- Seasonal Discount/Special Discount: This is a price reduction given by a producer or seller to buyers for special reasons such as end-of-season discounts, clearance sales, introduction of new products etc.
TERMS OF PAYMENT: The transactions between the seller and the buyer could be on a cash basis or credit basis. Cash transactions could be on the following basis:
- Cash on Delivery (COD)
- Cash with Order (CWO)
- Spot Cash: This is a condition where sellers and buyers are in physical contact and the buyer must pay cash for the goods bought from where (i.e. the spot) he takes over the goods.
- Prompt Cash: The buyer is requested in the case to pay for the goods within two or three days after which period he must have checked the goods and examined the invoice.
- Net Cash: This refers to the amount payable after all deductions and allowance have been made. It could also mean the amount payable when no deduction (i.e. discounts) are allowed.
COMMON ABBREVIATIONS
The common abbreviations found on the document listed earlier include
- & O. E. Errors and Omissions Excepted:- This is usually placed at the foot (bottom) of invoices, price list/ catalogue/quotations. It indicates that the details stated in the invoice or price list are not final and conclusive and that the seller reserves the right to correct any error or omission on the invoice or price list.
- A.T. (Value Added Tax):- This is charged on all sales and added as a percentage to the total amount shown on each invoice.
- Pd. (Carriage Paid):- This means that the goods are delivered free of charge to the buyer the seller bearing all expenses of transit and all risks up to the time of delivery at the prescribed destination.
- Fwd (Carriage Forward):- This implies that the buyer pays for the cost of transporting the goods.
- O.R. Kano:- This means “free on Rail up to Kano” i.e. the seller pays for the transportation of the goods by rail up to Kano from where the buyer bears all other freight if any.
- P.:- i.e. “per pro”, meaning “for and on behalf of” used when the document is being signed by someone other than the designated officer.
- Estimate/Tender:- This is a detailed estimate of a contract or construction work submitted in response to an advertisement.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- State five reasons why a trader usually grants discounts to his customers.
- State three differences between Cash Discount and Trade Discount
- Explain the terms (a) C.W.O. (b) E. & O.E.
GENERAL EVALUATION/REVISION QUESTIONS
1 State the difference between an ordinary invoice and a pro forma invoice
2 Explain the following terms used in connection with an invoice (a) 5% trade discount (b) net 3 months (c) E. & O. E. (d) carriage forward (e) 15% cash discount
3 State three characteristics of tramp vessels and two characteristics of ocean liners
4 Describe five different activities engaged in by people in commercial occupations
5 List five benefits of each of the following (a) branding (b) after-sales services (c) self
service (d) vending machine
READING ASSIGNMENT
- Essential Commerce for SSS by O.A. Longe, Page 135 – 146
- Comprehensive Commerce for SSS by J.U. Anyaele, Page 260-277
THEORY
- State three instances where the seller could issue a credit note to the buyer
- State three uses of the receipt
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will be learning about Means of Payment. We are very much eager to meet you there.
