Back to: MATHEMATICS SS2
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about the logarithm of numbers greater than and less than One. Enjoy the class!
The Logarithm of Numbers Greater than and Less than One
CONTENT
- Standard forms
- The logarithm of numbers greater than one
- Multiplication and divisions of numbers greater than one using Logarithm
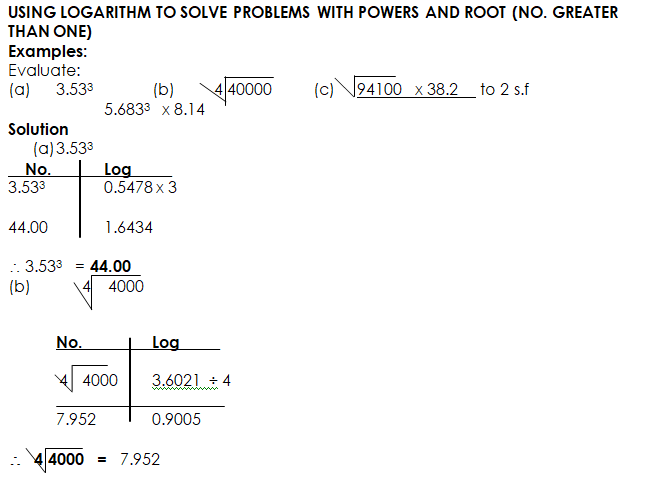
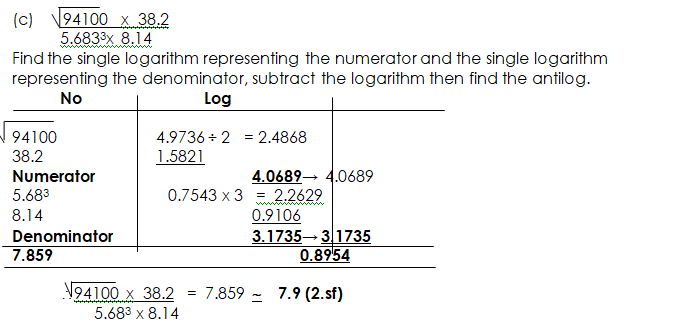
- Using logarithm to solve problems with roots and powers (no > 1)
- The logarithm of numbers less than one.
- Multiplication and division of numbers less than one using Logarithm
- Roots and powers of numbers less than one using Logarithm
STANDARD FORMS
A way of expressing numbers in the form A x 10x where 1< A < 10 and x is an integer, is said to be a standard form. Numbers are grouped into two. Large and small numbers. Numbers greater than or equal to 1 are called large numbers. In this case, the x, which is the power of 10 is positive. On the other hand, numbers less than 1 are called small numbers. Here, the integer is negative.
Numbers such as 1000 can be converted to its power of ten in the form 10x where x can be termed as the number of times the decimal point is shifted to the front of the first significant figure i.e. 10000 = 10

Note: One-tenth; one hundredth, etc. are expressed as negative powers of 10 because the decimal point is shifted to the right while that of whole numbers are shifted to the left to be after the first significant figure.
Examples
- Express in standard form (i) 0.08356 (ii) 832.8 in standard form
Solution
i 0. 08356 = 8.356 x 10-2
ii 832.8 = 8.328 x 102
- Express the following in standard form
(a) 39.32 = 3.932 x 101
(b) 4.83 = 4.83 x 100
(c) 0.005321 = 5.321 x 10-3
WORKING IN STANDARD FORM
Example:
Evaluate the following leaving your answer in standard form
- 4.72 x 103 + 3.648 x 103
- 6.142 x 105 + 7.32 x 104
- 7.113 x 10-5– 8.13 x 10-6
solution
(1) 4.72 x 103 + 3.648 x 103
= [4.72 + 3.648 ] x 103
= 8.368 x 10 3
(2) 6.142 x 105+ 7.32 x 104
= 6.142 x 105+ 0.732 x 105
= [6.142 + 0.732 ] x 105
= 6.874 x 105
(3) 7.113 x 10-5 – 8.13 x 10-6
= 7.113 x 10-5 – 0.813 x 10-5
= [ 7.113 – 0.813 ] x 10-5
= 6.3 x 10-5
Example: Simplify: √ [P/Q], leaving your answer in standard form given that
P = 3.6 x 10-3 and
Q = 4 x 10-8.
Solution

If a number is in its standard form, its power is its integer i.e. the integer of its logarithm e.g. log 7853 has integer 3 because 7853 = 7.853 x 103
Examples:
Use tables (log) to find the complete logarithm of the following numbers.
(a) 80030 (b) 8 (c) 135.80
Solution
(a) 80030 = 4.9033
(b) 8 = 0.9031
(c) 13580 = 2.1329
Evaluation
Use the table to find the complete logarithm of the following:
(a) 183 (b) 89500 (c) 10.1300 (d) 7
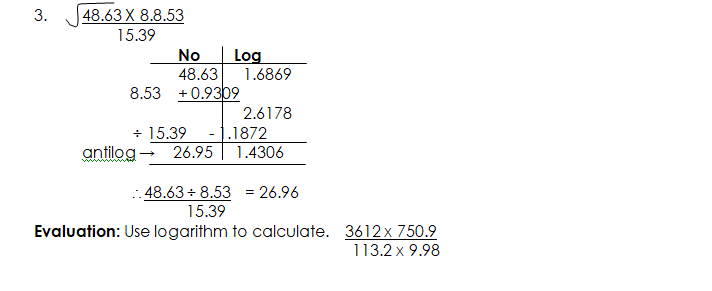
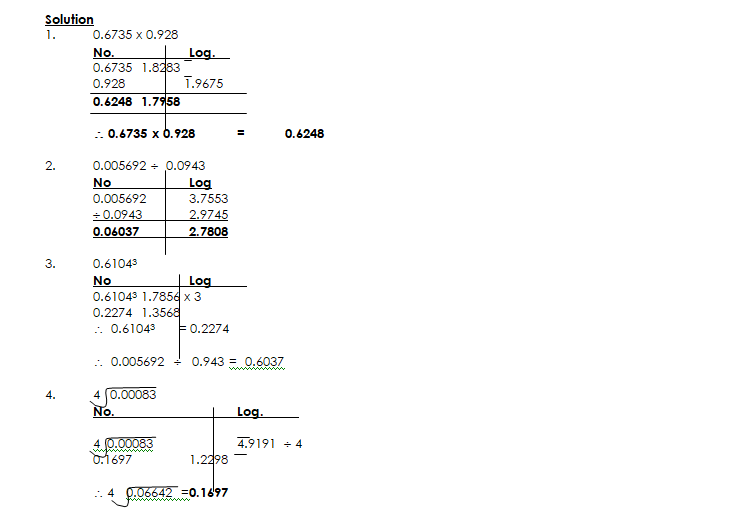
Multiplication and Division of numbers greater than one using Logarithm
To multiply and divide numbers using logarithms, first express the number as logarithm and then apply the addition and subtraction laws of indices to the logarithms. Add the logarithm when multiplying and subtract when dividing

LOGARITHM OF NUMBERS LESS THAN ONE
To find the logarithm of a number less than one, use negative power of 10 e. g.
0.037 = 3.7 x 10-2
= 10 0.5682 x 10-2
= 10 0.5682 + (-2)
= 10-2 5682
Log 0.037 = 2 . 5682
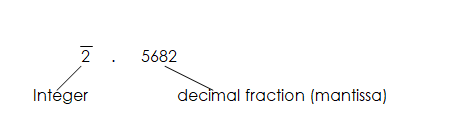
Example: Find the complete log of the following.
(a) 0.004863 (b) 0. 853 (c) 0.293
Solution
Log 0.004863 = 3.6369
Log 0.0853 = 2.9309
Log 0.293 = 1.4669
Evaluation
- Find the logarithm of the following:
(a) 0.064 (b) 0.002 (c) 0.802
- Evaluate using logarithm.
USING LOGARITHM TO EVALUATE PROBLEMS OF MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION, POWERS AND ROOTS WITH NUMBERS LESS THAN ONE
OPERATION WITH BAR NOTATION
Note the following when carrying out operations on the logarithm of negative numbers.
- The mantissa (fractional part) is positive, so it has to be added in the usual manner.
- The characteristic (integral part) is either positive or negative and should, therefore, be added or operated as directed numbers.
- For operations like multiplication and division, separate the integer from the characteristic before performing the operation.



In our next class, we will be talking about Percentage Error. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

From the power table above how is 0.01 be 10^-3?
thanks for the class
I really enjoyed it and it helped a lot
It’s a mistake. I noticed it
Am sorry am late to d group class
Thank u so much I love ur teaching
I don’t understand the antilog
No lesson for further Mathematics
Thanks
thank you for the wonderful lesson
This lesson is interesting
Thanks
Thanks for the class but that no ii 832.8
Ok
In the above question and use tables for to find the complete logarithm of the following numbers by number eight there is no on the statistic table statical table there’s no on the statical table there is no number eight on it so how are we going to find the number 8 logarithm
Finding the anti log is kind of confusing
good notes
This is actually a very good site and it helped me, thank you.
Pls can you help me evaluate 0.7685 multiplied by 0.03415
How are we going to get d log Of the number
Glad you found it helpful😊 For even more class notes, engaging videos, and homework assistance, just download our Mobile App at https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.afrilearn. It’s packed with resources to help you succeed🌟
I love the class,it is so interactive
We’re glad you found it helpful😊 For even more class notes, engaging videos, and homework assistance, just download our Mobile App at https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.afrilearn. It’s packed with resources to help you succeed🌟
Thank you so much for your great teaching
May God blessed your entire family
We’re glad you found it helpful😊 For even more class notes, engaging videos, and homework assistance, just download our Mobile App at https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.afrilearn. It’s packed with resources to help you succeed🌟
I DON’T STILL UNDERSTAND
Thanks for the class, I found it very interactive but I found a few problems with it. There were several typos that made it hard to get the point of the lesson. Fir instance, instead of 2. 2629
+0. 9106
I saw 2. 2629
+ 0. 9106
You see what I mean
TO MANY TYPIS. The lesson was good, but all the typos were making it hard to understand
We apologise about the typos. We’ll look into it. Thank you.
This class is very intresting
I don’t really understand how to divide when the number is less than 1
what a nice class it helps
FANTASTIC CLASS!
Thanks this is so useful 👍