Back to: COMPUTER SCIENCE SS2
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s Computer Science class, We will continue from where we stopped last class as we learn more about Computer Data Conversion (BUS). We hope you enjoy the class!

PRIMARY BUS
There are two buses within a computer;
Internal bus (also known as a front-side bus (FSB)) allows the processor to communicate with the system’s central memory (RAM).
Expansion bus (also known as input/output bus) allows various motherboard components to communicate with one another. However, it is mainly used to add new devices using what are called expansion slots connected to the input/output.
Functions of Buses in Computers
The functions of buses can be summarized as below:
1. Data sharing – All types of buses found on a computer must be able to transfer data between the computer peripherals connected to it.
The data is transferred in in either serial or parallel, which allows the exchange of 1, 2, 4 or even 8 bytes of data at a time. (A byte is a group of 8 bits). Buses are classified depending on how many bits they can move at the same time, which means that we have 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit or even 64-bit buses.
2. Addressing – A bus has address lines, which match those of the processor. This allows data to be sent to or from specific memory locations.
3. Power– A bus supplies power to various peripherals that are connected to it.
4. Timing– The bus provides a system clock signal to synchronize the peripherals attached to it with the rest of the system.
The expansion bus facilitates the easy connection of additional components and devices on a computer, for example, the addition of a TV card or sound card.
Bus Terminologies
Computers can be viewed to be having just two types of buses:
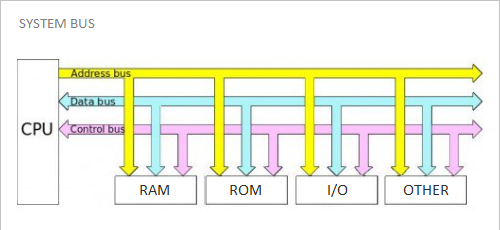
1. System bus:- The bus that connects the CPU to main memory on the motherboard. The system bus is also called the front-side bus, memory bus, local bus, or host bus.
2. A number of I/O Buses, (Acronym for input/output), connecting various peripheral devices to the CPU -these are connected to the system bus via a ‘bridge’ implemented in the processor’s chipset. Other names for the I/O bus include “expansion bus”, “external bus” or “host bus”.
Expansion Bus Types
These are some of the common expansion bus types that have ever been used in computers:
- ISA – Industry Standard Architecture
- EISA – Extended Industry Standard Architecture
- MCA – Micro Channel Architecture
- VESA – Video Electronics Standards Association
- PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnect
- PCMCIA – Personal Computer Memory Card Industry Association (Also called PC bus)
- AGP – Accelerated Graphics Port
- SCSI – Small Computer Systems Interface.
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will continue learning about Computer Files. We are very much eager to meet you there.

Dear Class Notes,
I really enjoy your class but please try to make it more specific and understandable with a lot of examples. Thank you!!
what is the meaning of computer bus?