Back to: AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE SS2
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s Agricultural Science class, We will be learning about Plant Nutrients and Nutrient Cycles. We hope you enjoy the class!

PLANT NUTRIENTS AND NUTRIENT CYCLES
CONTENT
- Classify plant nutrients
- Functions and deficiency symptoms of nutrients
- Nutrient cycles
PLANT NUTRIENTS AND NUTRIENT CYCLES
Plant nutrients are classified into two, these include macronutrient and micronutrient.
MACRONUTRIENTS
These are mineral elements or nutrients required by crops in large quantities. Examples are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium and sulphur.
MICRONUTRIENT OR TRACE ELEMENTS
These are mineral elements or nutrients required by crops in small quantities. Examples are Zinc, Copper, boron, molybdenum, Iron, Chlorine and Manganese.
FUNCTIONS AND DEFICIENCY SYMPTOMS OF PLANT NUTRIENTS
| S/N | ELEMENT | FUNCTION | DEFICIENCY SYMPTOMS |
| 1. | Nitrogen | i. Aids plant growth and reproduction ii. Promotes vegetative and short system growth iii. Excess Nitrogen delay maturation and fruiting iv. Promotes chlorophyll formation v. Necessary for the synthesis of plant hormones | i. Stunted growth ii. Yellowing of leaves iii. Leaves tend to drop iv. Poor formation of fruits and flowers |
| 2. | Phosphorus | i. It aid enzyme reactions ii. It is a constituent of cell division iii. Increases soil resistant to diseases iv. Helps in the ripening of fruits v. Help in root development and seed germination vi. Aids seed germination | i. Logging results in cereal crops ii. Stunted growth iii. Leaves turn purple and brownish in colour iv. Poor root development v. Immature fruit drop
|
| 3 | Potassium | i. An important constituent of plant tissues ii. Aids synthesis of carbohydrates iii. Activates various plant enzyme reactions iv. Promotes development of young plants v. Helps in nitrate uptake in the soil | i. Weak slender stems ii. Delayed growth iii. Premature loss of leaves iv. Brown colour at margin of leaves |
| 4 | Calcium | i. Strengthens plant cell with calcium pectate ii. Helps in translocation and storage of carbohydrate and proteins in seeds and tubers iii. Necessary for normal growth of root tips iv. It controls toxicity of aluminium, manganese and sodium ions v. It improves soil PH | i. Causes stunting of root system ii. Weak slender plants iii. Pale yellow colour of leaves |
| 5 | Magnesium | i. It is important in the synthesis of carbohydrate as it is a constituent of chlorophyll ii. It assists in the transportation of phosphate for fruit seeds development iii. It enhances plant growth iv. It is required for normal cell division v. Necessary for the synthesis of soil in plants | i. Chlorosis along leaf veins ii. Stunted growth Premature leaf fall |
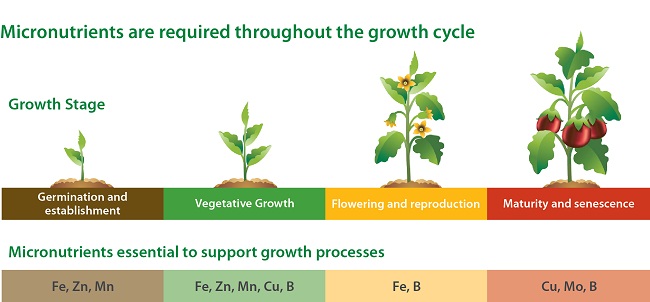
EVALUATION
- Give five examples each of macro and micronutrients.
- State the functions and deficiency symptoms of sulphur, iron, manganese copper, zinc, boron and molybdenum.
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will continue learning about Plant Nutrient and Nutrient Cycles. We are very much eager to meet you there.

It was wonderful one but their was no explanation on nutrient cycle
that was a wonderful teaching