Back to: GEOGRAPHY SS1
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about Nigeria: transportation and industries. Enjoy the class!
Nigeria: Transportation and Industries
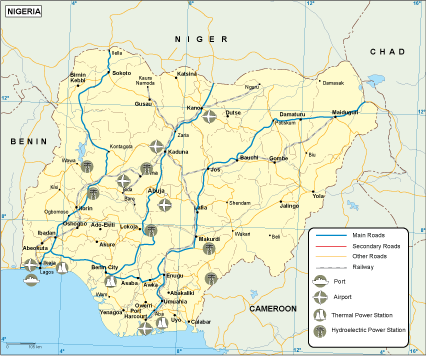
Transportation in Nigeria
Transportation is defined as the movement of people, goods and commodities from one place to another either by land, water or by air.
Types of transportation
Land transport:
This is the movement of people and goods from one place to another by land. Means of transportation by land include:
- Human portage: This involves the use of human legs for movement i.e. trekking. This is basically applicable where the distance is not much.
- Animal portage: This involves the use of certain animals like horse, donkey, camel, etc for movement. This is very common in the northern part of Nigeria.
- Road transport: This involves the use of motor cars, buses, motorcycles, Lorries and trucks for movement.
In Nigeria, there are 3 types of roads:
- Trunk A Road: These are roads constructed and maintained by the federal government. They are dual carriage or express roads linking federal and State capitals. E.g. Lagos – Ibadan, Warri – Benin, Onitsha – Enugu, Kaduna – Zaria express road.
- Trunk B Roads: Are roads constructed and maintained by the state government. They link different areas within a state. E.g. Ikeja – Ojota, Ogba – Oshodi, Mile 2 – Badagry, etc.
- Trunk C (local) roads: are roads constructed and maintained by the local government. In most cases, these roads are not tarred.
Advantages of road transportation
- It is the most common means of transportation.
- It provides door- to- door services.
- It makes goods available where they are scarce.
- It feeds water, rail and air transportation.
Disadvantages of road transportation
- Roads are very expensive to construct and maintain.
- The road is difficult to construct especially in the rainy season.
- Amount of goods and passengers carried by road is limited.
- Roads are more prone to accident than any other means of transportation
- They require adequate maintenance on a daily basis.
Limitations of road transportation
- Presence of high lands and other rugged relief.
- Presence of swampy areas.
- Soil erosion caused by heavy rain.
- Lack of finance to construct and maintain the roads.
Solutions
- Roads should be constructed on lowlands, passes or gaps around mountain areas.
- Construction of flyovers in marshy areas.
- Construction of bridges across rivers.
- A fund should be provided for road maintenance.
Rail transport:
This is transportation by rail i.e. the use of Trains. Nigeria uses mostly narrow-gauge railway lines.
Advantages of rail transport
- It is the most convenient means of transporting bulky goods.
- It is cheap.
- It can move people and goods over a very long distance.
- It helps to open up new lands.
Disadvantages of rail transport
- It involves the high cost of construction and maintenance.
- It is very slow (the slowest), and therefore not suitable for transporting perishable goods.
- Constant stopping in each station and changing of passengers waste a lot of time.
- It depends on roads to feed it with passengers.
Limitations of rail transport
- Rail transport is too slow.
- It has very low patronage and high competition with other forms of transport.
- Lack of spare parts, narrow-gauge with single tracks.
- Inadequate funding.
- Lack of technical know-how.
Solutions
- Modern rail system with wide gauges and multiple tracks should be developed.
- People should be trained in rail maintenance.
- Rail transport should be properly funded.
- Spare parts should be made available.
- Railway fare should be cheap to attract passengers
Evaluation
- Mention the types of transport.
- State the different types of road transport.
Air transport:
This is movement of people, goods and services from one place to another by air. It involves the use of aeroplanes, helicopters, jets and rockets. We have 2 types of Airports.
- International Airport and
- Local / Domestic Airports.
International Airports are airports where planes that fly outside the country can take off or land e.g. Muritala Mohammed International Airport (Lagos), Abuja International Airport (Abuja), Port Harcourt International Airport (PH).
Domestic (Local) Airports, on the other hand, are airports where planes that fly within the country i.e. from one state to another can take – off or land.
Advantages of air transport
- It is the fastest means of transport.
- It uses a direct route.
- It can reach anywhere provided there are landing facilities.
- Aeroplanes can cross mountain, dense forest and large ocean with ease and great speed.
- Urgently required Medicare supplies, machine parts, express mails, etc are easily dispatched by aeroplanes.
Disadvantages of air transport
- It is expensive to operate and maintain, especially the aircraft and airport facilities.
- It is very expensive (the most expensive).
- It is easily affected by bad weather, which makes visibility very poor.
- There is a problem of safety as the incidence of plane crashing and hijacking is becoming very common.
Limitations of air transport
- There is limited capital to construct an airport
- There is a problem of inadequate spare parts.
- Weather hazards.
- There is a problem of low patronage due to its expensive nature.
- There is also the problem of poor management and inadequate security.
Solutions
- Loans should be sourced for the proper maintenance of airports and aeroplanes.
- Spare parts should be procured.
- Efficient management should be adapted.
Evaluation
- State the advantages of air transport.
- What are the factors limiting the use of air transport?
Water transport:
This is the movement of people, goods and services by water. Water transport is divided into 2 parts
- Ocean navigation
- Inland water navigation.
Ocean navigation involves transportation by water between Nigeria other countries using the Oceans, especially along the coastline, while inland water navigation involves navigation along the creeks, lakes, lagoons and rivers in Nigeria.
Advantages of water transport
- It is the cheapest means of transport between countries.
- The ocean is free for all Nation to use.
- It is used to move bulky goods from one country to another during international trade.
- Cost of construction and maintenance is low and only restricted to ships and ports.
- It is good for transporting goods over a long distance.
- It is relatively safe.
Disadvantages of water transport
- It is the slowest means of transportation when compared to Air and Land transport.
- Cost of acquiring a ship is very high.
- Cost of ship parts, construction and maintenance is high.
- Lack of technical know-how
Limitations of water transportation
- Presence of waterfalls, rapids and cataracts limit the use of rivers.
- Presence of floating vegetation.
- It is only useful in countries with coastlines and parts as against landlocked countries with no oceans or seas
- Seasonality of most rivers is a problem.
- The shallowness of most rivers is also a problem.
- There is also a problem of seasickness.
- Limited capital to construct seaports
Solutions
- Rivers should be dredged regularly
- Loans should be granted to construct and maintain seaports.
- Medical facilities onboard should be improved.
- Construction of canals to bypass waterfall and cataracts.
Contributions of transportation to the economic development of Nigeria
- Movement of goods and services.
- Movement of people.
- Specific purposes e.g. Air transport could be used for a survey.
- National and International trade.
- Opening up of new land and areas.
- National integration.
- Development of tourism.
- Employment.
- Generation of revenue.
Problems of transportation
Physical factors:
- Presence of highlands
- Distance i.e. long distance
- Presence of marshy areas
- Presence of many rivers
- Soil erosion
- Poor visibility
Human factors:
- Lack of capital
- Lack of technical know-how
- Low patronage
- Bad roads
Evaluation
- Describe water transportation in Nigeria.
- State the disadvantages of this mode of transport.
- What are the problems facing transportation in Nigeria?
Industries in Nigeria
Manufacturing industry is defined as the industry that is involved in the turning of raw materials into new products by a mechanical or chemical process at home or in the factory.
Characteristic of manufacturing industries
- Most Nigeria industries rely on imported skilled labour from foreign countries.
- Most industries also depend on foreign countries for their raw materials.
- Industries are concentrated in few locations, especially in urban centres.
- Most manufacturing industries are mainly light industries.
- They are labour intensive i.e. require large labour.
- Their produce is mainly consumed in the local market.
- They are largely small scale.
Classification of manufacturing industries
Manufacturing industries can be grouped into 3 namely:
Light industries:
- They produce relatively lightweight goods such as matches, television sets, electric fans, books, etc.
- They employ mainly the services of women.
- They produce final or consumable goods.
Consumer goods industries:
- They turn raw materials into consumable goods.
- They are normally located in cities.
Heavy industries:
- They produce heavy or bulky goods.
- They employ the services of males mainly.
Examples include metallurgical industries, petroleum industries and shipbuilding industries.
Industries can also be classified into primary, secondary and tertiary industries based on their functions.
Primary industries:
- They are concerned with the extraction of raw materials provided by nature.
- They are also known as extractive industries.
Examples include mining, fishing, lumbering, farming and livestock production.
Secondary industries:
They are concerned with the turning of raw materials into finishing goods. Examples include construction, building, chemical industries, etc.
Tertiary Industries:
- They are concerned with the rendering of services.
- The service could be direct e.g. trading, banking, teaching, medical, etc
- The service could be indirect e.g. police, custom, soldiers, etc
Factors affecting the location of industries
- The proximity of the source of raw materials.
- Nearness to market.
- Nearness to sources of power.
- Availability of labour.
- Availability of capital.
- Adequate transport network.
- Government policies.
- Political stability.
Reasons why most manufacturing industries are sited in urban areas
- Large market
- Availability of labour
- Good transport network
- Nearness to seaports and airports
- Availability of finance
- Presence of infrastructure facilities.
Localization of industries
This refers to the sitting of industries in a particular area i.e. the concentration of industries in one area.
Advantages of concentration of Industries
- It leads to inter-dependence of industries
- It creates employment opportunities
- It aids mobility of labour
- It leads to the provision of social
- It encourages healthy competition among industries
- It leads to the development of an organized market e.g. cooperative societies
- It leads to attraction of subsidiary industries in the area
- It leads to inventions and innovations due to competition among industries.
Disadvantages of concentration of Industries
- It leads to congestion in traffic, industries and housing
- It can lead to a shortage of amenities
- It can escalate the crime rate like armed robbery, car snatching, etc
- It can cause environmental pollution due to the presence of many industries.
- The area is made the target of attack during wartime.
- It encourages rural-urban migration.
Evaluation
- What is an industry?
- Explain the different types of manufacturing industries in Nigeria.
- State the advantages of concentration of industries.
Contributions of the industrial sector to economic development
- Provision of employment opportunities
- Increase in Gross National Product (GNP)
- Infrastructural development
- Manpower development
- Funding for education and Research
- Improvement of trade balance
- Stimulation of other sectors.
Problems of manufacturing industries
- Shortage of raw materials
- Insufficient capital
- A high degree of foreign dependence
- Poor quality of industrial labour
- Political instability
- Poor management
- Competition from foreign goods
- Inadequate power supply
Solutions to industrial problems
- Acquisition of skills
- Good government policies
- Active government participation
- Incentives to local industries
- Provision of transport facilities
- Creation of industrial zones
- Stable government.
Local craft (cottage) industries in Nigeria
Local craft or cottage industries are those industries that depend mainly on raw materials obtained from their immediate locality. They use simple tools and their work is of high artistic quality. They include:
- Leatherworks e.g. sandals, cushions, handbags, etc. They mostly found in Kano, Bida and Sokoto.
- Wood carving: This is done in Ikot Ekpene, Uyo, Oyo, Benin city, etc
- Pottery and glass making: These are done in Ikot Ekpene, Bida, Ilorin and Calabar.
- Ropes and mat making: These are done in Ikot Ekpene, Warri, and Kano.
- Brass and silver works: These are done in Bida, Benin and Kano
- Textile/cloth weaving: These are done in Akwette, Okene, Kano, and Iseyin
Modern manufacturing industries in Nigeria
- The western industrial zone: Include Lagos, Ibadan, Sango-Ota, Abeokuta, Epe, Apapa, Ewekoro, Oshogbo etc.
- The south-east industrial zone: Include Nkalagu, Onitsha, Port Harcourt, Enugu, Aba, Owerri, Calabar, etc.
- The north-central industrial zone: Include Kano, Kaduna, Jos, Zaria, etc.
- The mid-western industrial zone: Include Warri, Benin, Sapele, Ughelli, etc.
General evaluation
- What is transportation?
- State the mode of transportation.
- Which transport mode is considered the cheapest?
- State the advantages of land transport.
- Explain the classification of manufacturing industries in Nigeria.
In our next class, we will be talking about Nigeria: Population. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

I enjoy this class l cannot wait for the next class