Back to: BUSINESS STUDIES JSS2
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s Business Studies class, We will be discussing Trade. We hope you enjoy the class!

Trade
Meaning of trade:
Trade is the buying and selling of goods and services. It involves the direct exchange of goods and services for money or other goods, which is called barter. It is the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, following payment or exchange of goods. It is sometimes called commerce or financial transaction or even barter. A network that allows trade is called a market.
Trade is an important factor of production because, in its absence, the producer or manufacturer will not do business, since every business is set up to make profit.
Importance of trade
- Trade enhances the production of goods and services.
- It creates employment even for people who cannot read or write.
- It gives room for a variety of items to be produced.
- It creates a relationship between buyers and sellers.
- It helps in the growth of industries.
- It brings people of diverse culture and languages closely.
- It brings development to a country.
- It enhances the movement of people from one place to another.
- It promotes communication.
- It brings technology closer to people.
Forms of trade
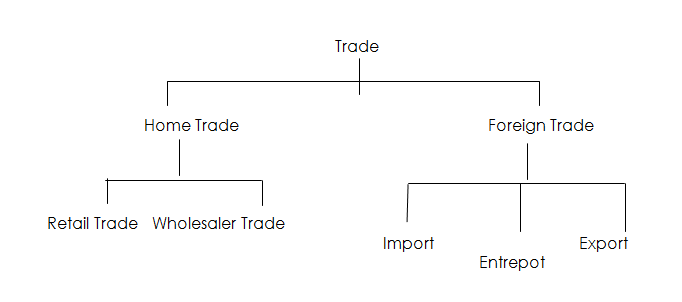
Trade is divided into two main parts: home trade and foreign trade.
A) home trade:
This is the exchange of goods or the buying and selling of goods and services within a country. It is also known as domestic or internal trade and has two sub-divisions, wholesale trade and retail trade.
- Wholesale trade: this involves buying goods in large quantity from the manufacturer/producer and selling in small quantities to the retailers. A person who does this is known as a wholesaler. The wholesaler is oftentimes called the middleman because he is in between the producer and the retailer.
- Retail trade: in this form of home trade, goods are bought in small quantities from the wholesalers or sometimes direct from the manufacturer and sold in units to the public or final consumers. A retailer is a person who buys goods from the wholesaler or directly from the manufacturer and sells them in small quantities to the final consumers.
B) foreign trade:
This is the exchange, buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries of the world. It is also known as international trade or external trade. Like home trade, foreign trade is divided into three groups. They are import trade, export trade and entrepôts trade.
- Import Trade: this is the bringing in of goods and services, knowledge and technology into a country from another country.
- Export trade: this is the selling of a country’s home-made goods and services to other countries of the world.
- Entrepot: this type of trade involves the importing and re-exporting of goods, it is a trade of buying goods from a country and the goods are not sold in the country of import, but rather exported to other countries. For example, you import goods into a country, then you also export that goods to another country, that is “entrepot…”
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will be talking about Aids to Trade. We are very much eager to meet you there.
