Back to: COMPUTER SCIENCE JSS2
Welcome to JSS2!
We are eager to have you join us in class!!
In today’s class, We will be discussing CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS. We are conversant with the computer system, but this serves as a reminder on the classification of computers. We hope you enjoy the class!
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
Computers can be classified into four:
- By generation
- By type
- By size
- By purpose
By Generation:
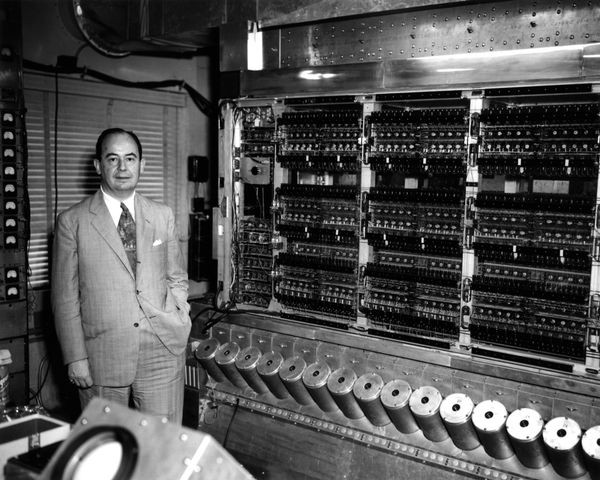
First Generation (1940 – 1956 ):
They were developed during the second world war to design flying bombs and missiles for the war. Examples are Colossus, ENIAC, EDVAC, EDSAC, UNIVAC, etc.
Features
- It uses vacuum tubes
- They are very big
- It generates lots of heat
- They are very slow in processing information
- It uses a magnetic drum for memory
- They occupy large space
- It uses punch cards for input and output
Second Generation (1956 – 1963 ):
These computers use transistors in place of vacuum tubes after the second world war e.g. IBM 7090.
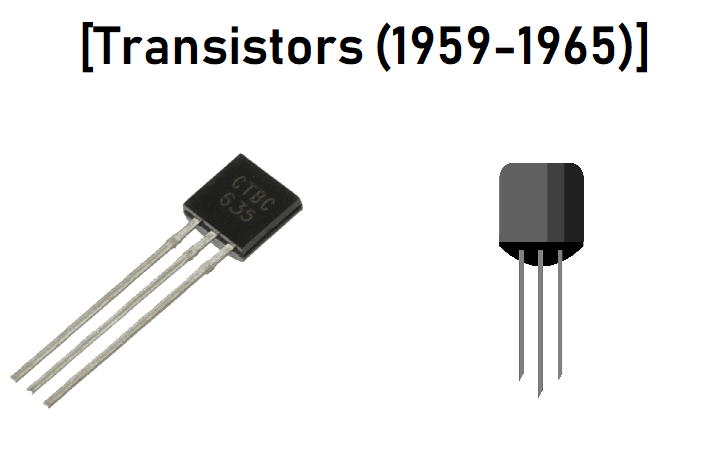
Features
- It uses transistors
- It is smaller in size
- Faster in processing information
- It is cheaper to get
- It consumes less energy
- More reliable
- It uses punch cards for input and output

Third Generation (1964 – 1971 ):
They are I.Cs (Integrated Circuit) computers. Transistors are minimized and placed on silicon chips.
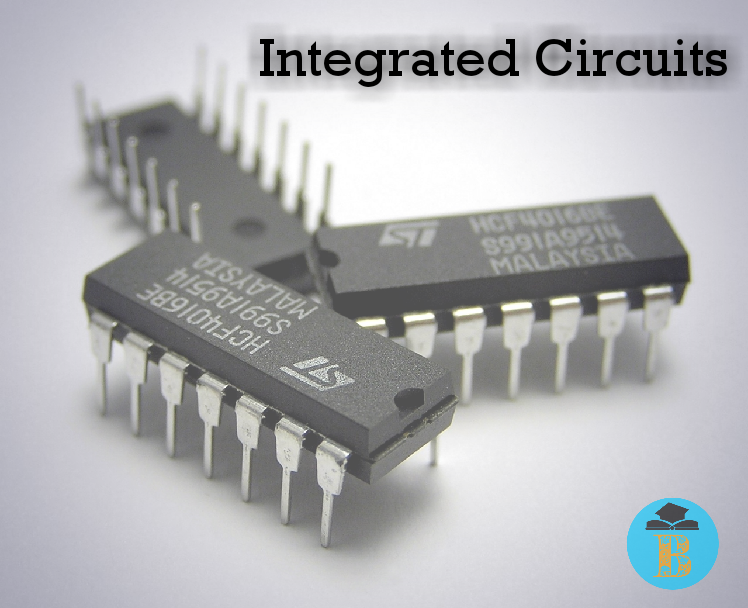
Features
- It uses integrated circuit
- Keyboard and monitors were used as input and output devices
- It uses an operating system eg: Microsoft OS, Mac OS etc.
- Enhanced processing speed
Fourth Generation (1972 – 1989):
This generation of computer uses a microprocessor, the era of CPU came to surface. Example: Micro Computer.
Features
- It uses microprocessors
- ADA programming language was developed
- It is a personal system
Fifth Generation (1991 – date):
These computers use artificial intelligence. They have voice recognition and are capable of doing more work e.g. Robot.
By Type:
Analog Computer:
They give their result is in continuous value rather than discrete value. They are built to respond to continuous signals such as electricity, temperature, pressure e.g. speedometer, wall clock, etc.
Digital Computer:
The word digital means discrete or whole number. Digital computers function by accepting and manipulating data in the form as discrete binary numbers e.g. digital thermometer, calculators, etc.
Hybrid Computer:
They combine the proper of both analog and digital computers. This means that they can accept and process data and produce output both in digital and analog formats.
By Size:
Computers can be classified by size, they are microcomputer, minicomputer, mainframe computer and supercomputers.
1. Micro Computers:
They are the smallest class of computers. It uses a single microprocessor mounted with memory chips as its central processing unit e.g. desktop, laptops, etc.
2. Minicomputers:
These are middle-level computers built to perform complex computations.
3. Mainframe Computers:
These are the largest class of computers. They have multiple chips so they can sustain a large amount of processing and allow many users at the same time.
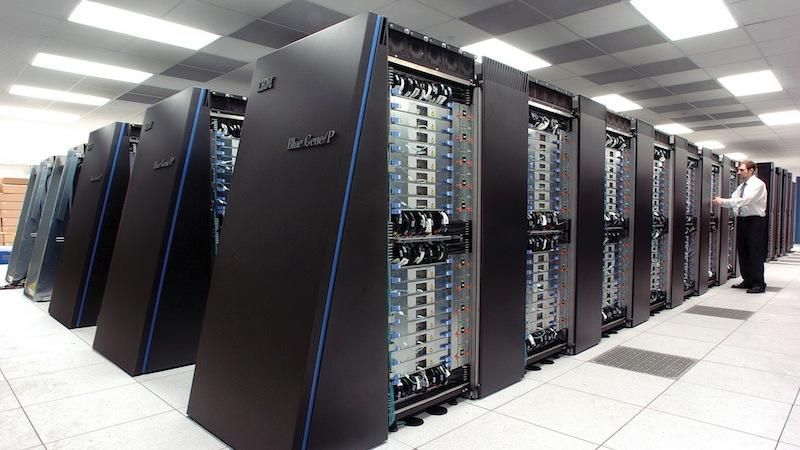

4. Super Computers:
They are the largest and fastest types of mainframe computers. They perform highly complex and time-consuming computations and are used heavily by scientists, large business and the military for large research work such as weather forecasts, oil explorations, etc.
By Purpose:
1. General Purpose Computers:
They are designed to solve a wide range of problems. They perform many functions because various types of application programs are stored in them e.g. Microcomputers.
2. Special Purpose Computers:
They are designed to solve a specific problem e.g. ultrasound machines, x-ray machines, fuel dispenser, etc.
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will be talking about The Computer System. We are eager to meet you there.
