Back to: PHYSICS SS3
Welcome to class!
In today’s class, we will be talking about electromagnetic waves. Enjoy the class!

Electromagnetic waves are those waves in which there are sinusoidal variations of electric and magnetic field vectors at right angles to each other as well as at right angles to the direction of wave propagation.
Sources of electromagnetic waves
Accelerated charges radiate electromagnetic waves. An oscillating charge is an example of an accelerating charge. Electromagnetic waves are also produced when fast-moving electrons are suddenly stopped by a metallic surface of high atomic number.
Electromagnetic waves properties
- These waves do not require a medium for propagation and they are transverse in nature.
- These waves propagate through space with the speed of light in vacuum.
- The wave having higher the frequency, will have the higher energy associated with it.
- It can be used to carry information.
- It travels in straight lines.
- It can be split and recombined to form interference / Diffraction pattern.
- It can be reflected or refracted.
- They obey the wave equation (v = λ f).
Nature of electromagnetic waves
Electric and magnetic fields oscillate sinusoidally in space and time in an electromagnetic wave. The oscillating electric and magnetic fields, E and B are perpendicular to each other, and to the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave. For a wave of frequency ν, wavelength λ, propagating along the z-direction, we have
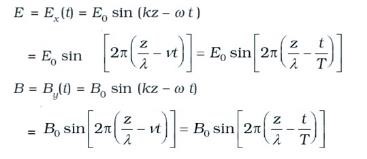
Speed of electromagnetic wave
The speed c of an electromagnetic wave in vacuum is related to μ0 and ε0 (the free space permeability and permittivity constants) as follows:
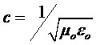
Electromagnetic waves other than light also have the same velocity c in free space.
The speed of light, or of electromagnetic waves in a material medium is given by
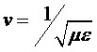
where μ is the permeability of the medium and ε its permittivity.
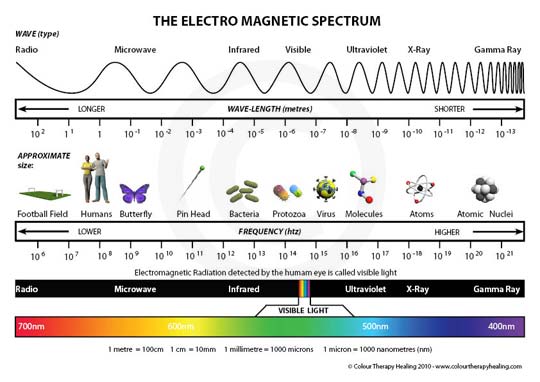
Electromagnetic spectrum
An arranged array of electromagnetic radiations in the sequence of their wavelength or frequency is called an electromagnetic spectrum. The electromagnetic spectrum is made of radio waves, infrared radiation, visible (light) rays, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, gamma (g) rays, etc. they can also be represented in their first alphabet as RIVUCG in their correct order.
| R | I | V | U | X | G |
| Radio rays | Infrared rays | Visible (light) rays | Ultraviolet rays | x-rays | Gamma rays |
Increasing velocity, decreasing wavelength, increasing frequency.
Electromagnetic spectrum
| Radiation | Wavelength (m) | Frequency (Hz) |
| Radio waves | 103 | 104 |
| Infrared rays | 10-6 | 1010 |
| Visible (ROYGBIV) | (4.5 – 7.0) x 10-7 | 1012 |
| Light Ultraviolet | 10-8 | 1014 |
| X-rays | 10-10 | 1016 |
| Gamma rays | 10-12 | 1018 |
Radio waves
Radio waves are produced by the accelerated motion of charges in conducting wires.
Uses
- They are used in radio and television communication systems.
- They are generally in the frequency range from 500 kHz to about 1000 MHz.
Microwaves
Microwaves (short-wavelength radio waves), with frequencies in the gigahertz (GHz) range. They are produced by special vacuum tubes (called klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn diodes).
Uses
- Due to their short wavelengths, they are suitable for the radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
- Microwaves are also used in radio and TV communication.
Infrared waves
Infrared waves are sometimes referred to as heatwaves.
Infrared waves are produced by hot bodies and molecules.
Infrared radiation plays an important role in maintaining the earth’s warmth or average temperature through the greenhouse effect.
Uses
- Treat muscular strain
- For taking photographs in fog or smoke
- In greenhouse to keep plants warm
- In weather forecasting through infrared photography
Ultraviolet rays
It covers wavelengths ranging from about 4 × 10–7 m (400 nm) down to 6 × 10–10 m (0.6 nm).
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is produced by special lamps and very hot bodies.
The sun is an important source of ultraviolet light.
Ultraviolet radiations can be focussed into very narrow beams for high precision applications such as LASIK (Laser-assisted in situ keratomileuses) eye surgery.
Ultraviolet lamps are used to kill germs in water purifiers
Uses
- In the study of molecular structure
- In sterilizing the surgical instruments.
- In the detection of forged documents, fingerprints.
Visible rays
It is the part of the spectrum that is detected by the human eye.
It runs from about 4 × 1014 Hz to about 7 × 1014 Hz or a wavelength range of about 700 – 400 nm.
Uses
- Visible light emitted or reflected from objects around us provides us with information about the world.
X-rays
It covers wavelengths from about 10‒8 m (10 nm) down to 10‒13 m (10‒4 nm).
One common way to generate X-rays is to bombard a metal target by high energy electrons.
X-rays are used as a diagnostic tool in medicine and as a treatment for certain forms of cancer.
Uses
- In detecting faults, cracks, flaws and holes in metal products.
- In the study of a crystal structure.
- For the detection of pearls in oysters.
Gamma rays
The wavelengths of Gamma rays are from about 10‒10 m to less than 10‒14 m.
Gamma rays are produced in nuclear reactions and also emitted by radioactive nuclei.
Uses
- They are used in medicine to destroy cancer cells
- Rays are used for the study of nuclear structure
General evaluation
- What are electromagnetic waves? Give three examples of it.
Assignment
- List six electromagnetic radiations.
- State the uses of each
- Explain electromagnetic spectrum, stating its function and arrange the spectrum in accordance with an increase in wavelength and decrease in frequency.
In our next class, we will be talking about Electromagnetic Induction. We hope you enjoyed the class.
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.

this is interested how will i pay for the others
Thanks so for nice work. This is interesting
Really interesting
Very good note
I love it so much and is interesting
What will I do so as to have video lesson?
To access the video lesson, simply download the Afrilearn App here https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.afrilearn&hl=en_CA&gl=US or visit https://myafrilearn.com/
Do I need to access the class with data??
Thanks sooo much it is fascinating
I enjoyed it thanks very much
Thanks sooo much. It is fascinating
I really love it I’m so excited and interested on it
I really love it so excited and interesting