Back to: ENGLISH LANGUAGE JSS3
Welcome to Class !!
We are eager to have you join us !!
In today’s English Language class, We will be working on our Grammer as we learn about Phrases and Clauses. We hope you enjoy the class!

Phrases and Clauses
- What is a phrase?
- Types of phrases
- What is a clause?
- Types of clauses
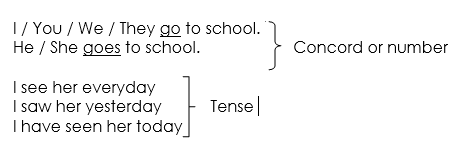
A phrase is a group of words which does not contain a finite verb. A finite verb marks for tense, number and concord.
Examples of finite verbs are:
Types of phrases
A phrase can be:
(i) NOUN PHRASE (NP)
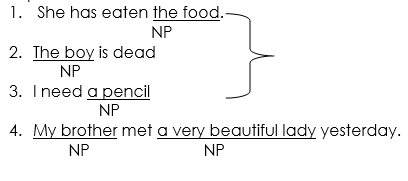
A noun phrase is a group of words which has a noun or pronoun as its headword.
Examples
A noun phrase can function as:
- The subject of the sentence – as in 2 above
- The object of the sentence- as in 1 above
- Subject complement e.g.
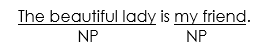
“My friend” is the subject complement
- Object complement e.g.

“Our class captain” is the object complement
- The complement of a preposition e.g.

“The man” is a complement of the preposition “to”
(ii) VERB PHRASE (NP)
A verb phrase can either be simple or complex. It is simple when it is made up of just one main/ lexical verb. A verb phrase, however, becomes complex when it consists of one main verb and one or more auxiliary verbs.
Examples:

A verb phrase performs the function of a verb- tells us the action performed
(iii) ADVERBIAL PHRASE: (AP)
An adverbial phrase is a group of words headed by an adverb.
An adverbial phrase can be realized by:

(iv) ADJECTIVAL PHRASE (Adj ph)
An adjectival phrase describes/ qualifies a noun or pronoun.
Examples:

(v) PREPOSITIONAL PHRASE (p. ph)
Examples
CLAUSES
A clause is a group of words that contains a finite verb. Clauses can be:
- Main clause/ independent clause and
- Subordinate clause / dependent clause
An independent clause can stand on its own to express full meaning while a subordinate clause cannot.
Consider the following sentences
Independent clause / subordinate clause
(a) I saw a dead man / when I was coming to school today.
(b) She didn’t see the pencil / where she kept it.
Subordinate clauses are of three types, namely:
- Noun clause
- Adjectival clause
- Adverbial clause
(a) Noun clause: (NC) Upper case
This is a subordinate clause that performs the functions of a noun. i.e.
- The subject of the sentence as in:
- The object of the sentence as in:
- Subject complement, as in:
- Object complement, as in:
- The complement of a preposition as in:
- The prize goes to whoever wins.
NC
(b) ADJECTIVAL CLAUSE (Adj. cl.)
An adjectival clause performs the function of an adjective .i.e. describes or qualifies a noun or pronoun.
Examples
- This is the boy who stole my money.
Adj. cl.
- That is the house which my father just bought.
Adj. cl.
- These are the children whose parents died in fire-accident last week
Adj. cl.
(c) ADVERBIAL CLAUSE
An adverbial clause performs the function of an adverb i.e., it modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb. We have adverbial clause of time, reason, place, purpose, manner, condition, result, degree, concession etc.
Examples
- He came back when I had slept.
Adv. cl.
2) She goes whereas she likes.
Adv. cl.

Evaluation
Identify the phrases in the sentences below:
- The car is in the garden.
- The girl with the blue bag is my sister.
- The man came at the wrong time.
- She has done the work
- He gave the book to me
Reference: Count down English by Ogunsanwo
Reading Assignment: Read Count down English by Ogunsanwo pages 220- 225; English Grammar by Sam Onuigbo
We have come to the end of this class. We do hope you enjoyed the class?
Should you have any further question, feel free to ask in the comment section below and trust us to respond as soon as possible.
In our next class, we will be reading the Comprehension: The fall of Seyfawa Dynasty in Borno. We are very much eager to meet you there.

I like it
Love ❤️ your lesson my friends will need some help with their studies and this class is perfect for them ❤️❤️🧑🧑🧒🧒❤️
love you lessons it helps me to understand more on grammar tenses
I really appreciate you, thank you.
i love the class 😀 thanks
I enjoye this class